111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

VEGFR2 选择性抑制剂在胃癌中的免疫介导的抗肿瘤作用
Authors Yang J, Yan J, Shao J, Xu Q, Meng F, Chen F, Ding N, Du S, Zhou S, Cai J, Wang Q, Liu B
Received 5 October 2019
Accepted for publication 31 October 2019
Published 15 November 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 9757—9765
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S233496
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Isha Chandra
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
Background: It was previously reported that targeting vascular epithelial growth factor (VEGF)/VEGFR could modulate the antitumor immunity. VEGFR2 inhibitor YN968D1 is a highly selective VEGFR2 inhibitor and was approved for the treatment of late-stage gastric cancer in 2014, but its role in antitumor immunity remains unknown.
Materials and methods: In this study, we investigated the effects of YN968D1 on the function of T cells in vitro by testing the cytotoxicity and cytokine production. Next, we constructed peritoneal dissemination and subcutaneous gastric cancer mouse model to assess the cytotoxicity of YN968D1-treated T cells in vivo, respectively.
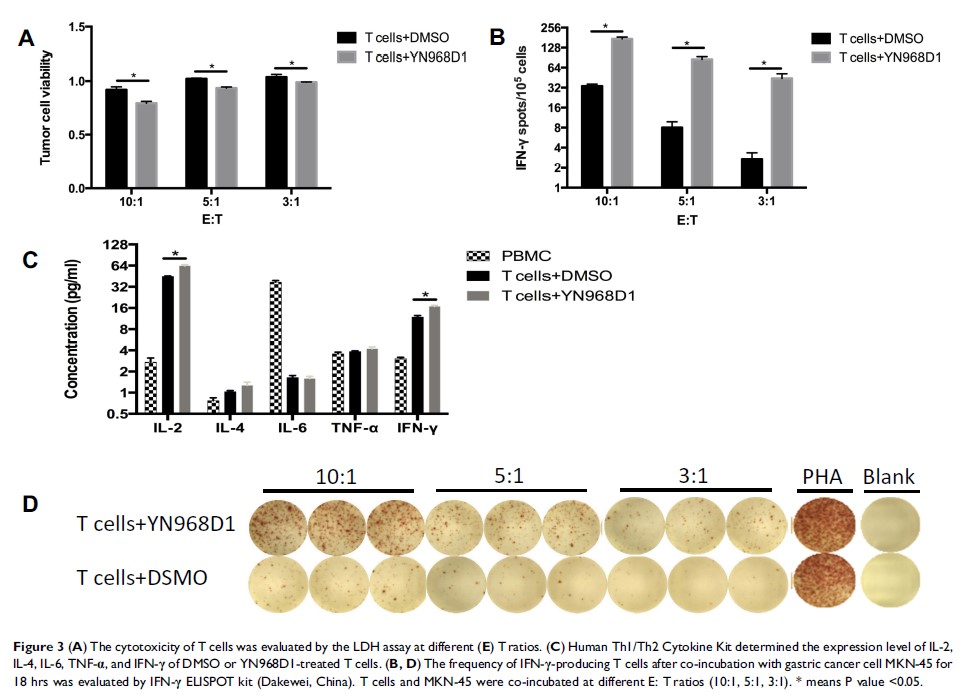
Results: We found that the use of YN968D1 in CD8+ T cells could reduce the expression levels of inhibitory checkpoints, such as Lag-3, PD-1, and Tim3, escalate the production of IFN-γ and IL-2 and promote the cytotoxicity of T cells dramatically in vitro. The transfer of YN968D1-treated T cells achieved better tumor control compared to DMSO-treated T cells or control in both peritoneal dissemination and subcutaneous gastric cancer mouse models.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that YN968D1 can enhance the T cell-mediated antitumor immunity.
Keywords: YN968D1, gastric cancer, T cells, cytotoxicity, anti-tumor immunity