111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

木犀草素通过调节信号转导子和转录激活因子 3 介导的炎症反应减轻动脉粥样硬化
Authors Ding X, Zheng L, Yang B, Wang X, Ying Y
Received 28 February 2019
Accepted for publication 26 September 2019
Published 18 November 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 3899—3911
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S207185
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tin Wui Wong
Background: Inflammatory factors play a crucial role throughout the development and progression of atherosclerosis, which has been considered as a chronic vascular inflammatory disease. Luteolin, a natural flavonoid which exists in many natural medicinal materials, has anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic and other pharmacological effects. Recently, the protective effects of luteolin on the cardiovascular disease have been reported. However, there is a paucity of studies on anti-atherosclerosis. Therefore, the anti-atherosclerosis potential of luteolin remains to be elucidated.
Method: ApoE-/- mice were fed with a high-fat diet to induce atherosclerosis in an animal model, where they were treated with oral administration of luteolin for 12 weeks. Primary mouse peritoneal macrophages challenged with oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) were used for in vitro mechanistic study. The effectiveness of luteolin in the ApoE-/- mouse model of atherosclerosis was estimated in the aortic sinus and enface, and the underlying mechanisms were explored by molecular modeling study and siRNA-induced gene silencing.
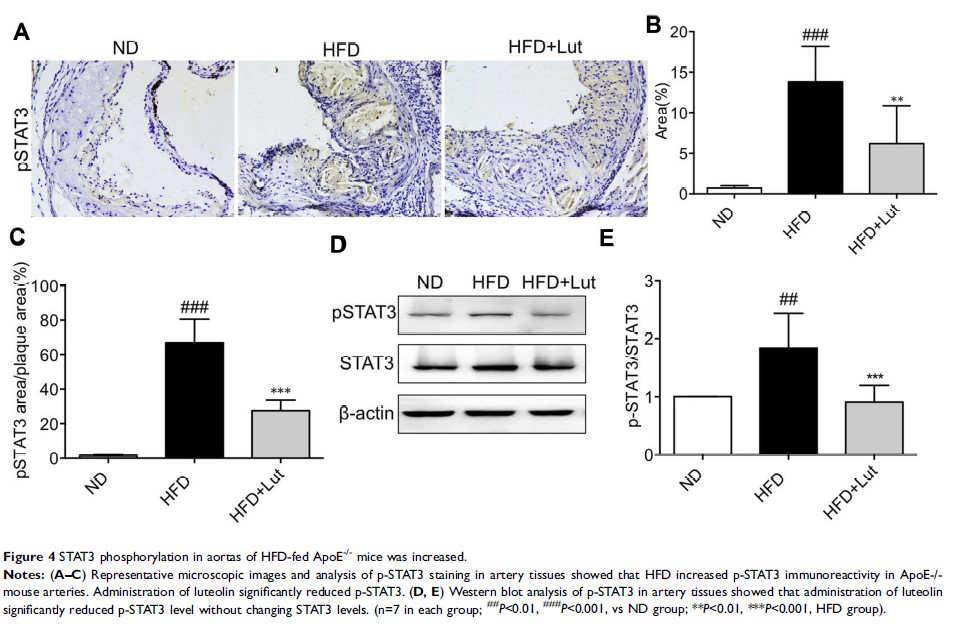
Results: Our results showed that luteolin remarkably attenuated atherosclerosis in high-fat diet-induced ApoE-/- mouse via alleviating inflammation. We further found that luteolin decreased oxLDL-induced inflammation by inhibiting signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) in vitro, respectively. Further molecular modeling analysis indicated that luteolin interacted with STAT3 primarily through hydrogen bond interaction.
Conclusion: Luteolin could be a promising candidate molecule for atherosclerosis, and STAT3 may be a potential therapeutic target that could prevent the development of atherosclerosis.
Keywords: atherosclerosis, luteolin, inflammation, transducer and activator of transcription 3