111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

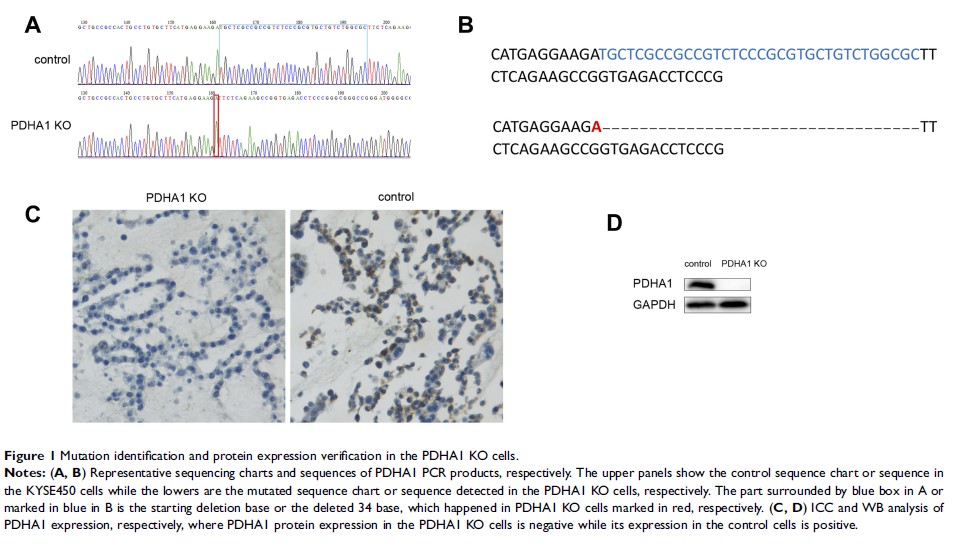
人食管鳞状细胞癌细胞中的 PDHA1 基因敲除导致更大的 Warburg 效应和体内外攻击特征
Authors Liu L, Cao J, Zhao J, Li X, Suo Z, Li H
Received 12 August 2019
Accepted for publication 31 October 2019
Published 18 November 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 9899—9913
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S226851
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Sandhya Gopi
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leo Jen-Liang Su
Background: One of the remarkable metabolic characteristics of cancer cells is that they prefer glycolysis rather than oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 alpha subunit (PDHA1) is an important prerequisite for OXPHOS. Our previous studies have shown that low level of PDHA1 protein expression in esophageal squamous cell cancer (ESCC) was correlated with poor prognosis. However, the effect of PDHA1 inhibition on metabolism and biological behavior of esophageal cancer cells remains unclear.
Methods And Results: In this study, a KYSE450 PDHA1 knockout (KO) cell line of esophageal cancer was established by CRISPR/Cas9 technology. Then, the glycose metabolism, cell proliferation and migration abilities, chemotherapeutic tolerance and angiogenesis of the PDHA1 KO cells were investigated in vitro and in vivo. In the PDHA1 KO cells, the glycolysis and the consumption of glucose and glutamine were significantly enhanced, while the OXPHOS was significantly suppressed, implying Warburg effect in the PDHA1 KO cells. Furthermore, it was also proved in vitro experiments that the PDHA1 KO cell obtained proliferation advantage, as well as significantly greater chemotherapy tolerance and migration ability. Xenograft experiments discovered not only larger tumors but also increased angiogenesis in the PDHA1 KO cell group.
Conclusion: Inhibition of PDHA1 gene expression in human ESCC leads to metabolic reprogramming of Warburg effect and increased malignancies. Targeting ESCC metabolic reprogramming may become a potential therapeutic target.
Keywords: PDHA1, ESCC, Warburg effect, CRISPR/Cas9, xenotransplantation, KYSE450