111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

对糖原合成酶激酶-3β 活性的遏制可通过下调 Brachyury 表达来抑制颅底脊索瘤细胞的生长和存活
Authors Yan X, Li Z, Li H, Liu P, Zhao Z, Cheng S, Wang Z, Zhang Q
Received 11 June 2019
Accepted for publication 31 October 2019
Published 18 November 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 9783—9791
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S218930
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Shreya Arora
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
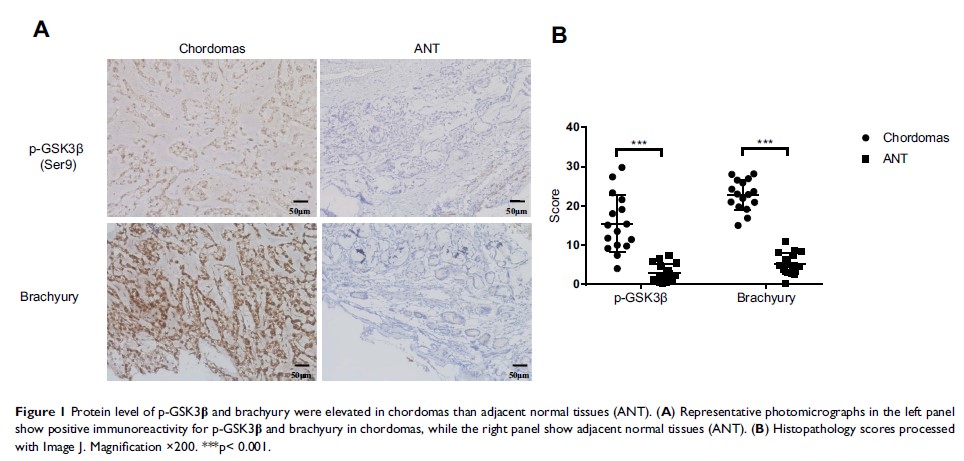
Purpose: Chordomas are locally aggressive tumors arising from notochordal remnants. Brachyury, a protein coded by T-gene, is crucial for chordoma cell proliferation. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3β) activity on brachyury expression and on the growth and survival of skull base chordoma cells.
Patients and methods: In this study, 16 paraffin-embedded specimens of primary skull base chordomas were analyzed for the expression of phosphorylated GSK3β and brachyury using immunohistochemistry. The UM-Chor1 cell line derived from a clival chordoma was treated with AR-A014418 (AR), an inhibitor of GSK3β, and brachyury expression was analyzed by qRT-PCR and Western blotting. The possible mechanism by which brachyury regulates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway was investigated by immunocytochemistry. The effects of AR on cell proliferation as well as sensitivity to chemotherapeutic drugs were also examined.
Results: The results suggested that phosphorylated GSK3β and brachyury were upregulated in chordoma tissues. The GSK3β inhibitor (AR) decreased brachyury expression and suppressed the growth and survival of the chordoma cells, possibly via regulation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Moreover, AR increased the sensitivity of chordoma cells to chemotherapeutic drugs in vitro.
Conclusion: This study provides evidence for the clinical development of the GSK3β inhibitor (AR-A014418) as a potential chemotherapeutic adjuvant for the treatment of chordoma.
Keywords: GSK3β inhibitor, skull base chordoma, brachyury, Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway