111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

雷替曲塞配合以奥沙利铂为基础的肝动脉化疗栓塞来治疗无法切除的肝细胞癌的疗效和安全性
Authors Shao W, Li C, Tang J, Song J, Li Z, Sun J, Xu Y, Zheng Z, Cao J, Zhang L
Received 29 May 2019
Accepted for publication 22 October 2019
Published 19 November 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 9863—9869
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S217524
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Nicola Ludin
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of raltitrexed plus oxaliplatin-based transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
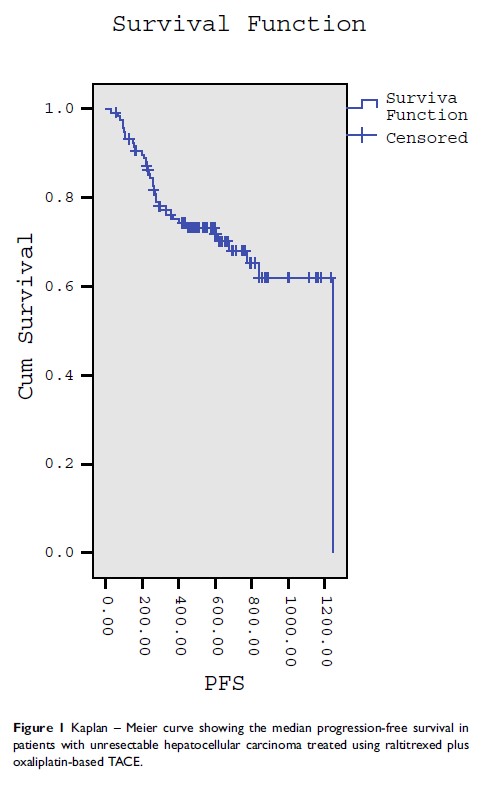
Methods: A total of 123 patients with unresectable HCC were recruited into the prospective cohort study. Raltitrexed plus oxaliplatin-based TACE was performed according to the traditional method at monthly intervals and was repeated for up to 4 cycles if no disease progression or intolerable toxicity occurred. The primary efficacy endpoint was overall survival (OS), and the secondary endpoints were progression-free survival (PFS) and tumor response rate. The Cox proportional-hazards regression model was used to assess the independent prognostic factors of OS. Adverse events were also observed.
Results: The median OS time and PFS were 623 days (95% CI: 461, 785) and 338 days (95% CI: 302, 704), respectively. The disease control rate was 95.5% (118/123). The Cox proportional-hazards regression model indicated that age, ECOG performance status and response to TACE as independent prognostic factors of OS. No treatment-related mortality occurred within 30 days of treatment procedure. The most common complications included postembolization syndrome, liver dysfunction and hematological toxicity. Grade 3 pain, transglutaminase abnormality and thrombocytopenia were observed in 16 (13%), 15 (12.2%) and 3 (2.4%) patients, respectively. No grade 4 adverse events were observed.
Conclusion: Raltitrexed plus oxaliplatin-based TACE led to high tumor response rate and promising PFS and OS, and was considered safe and tolerable in patients with unresectable HCC.
Keywords: raltitrexed, oxaliplatin, hepatocellular carcinoma, transarterial chemoembolization