111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

低浓度的紫杉醇(PTX)和 RSL3 通过诱导突变体 p53 的铁死亡抑制下咽鳞癌肿瘤细胞的生长
Authors Ye J, Jiang X, Dong Z, Hu S, Xiao M
Received 31 May 2019
Accepted for publication 13 October 2019
Published 20 November 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 9783—9792
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S217944
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Nicola Ludin
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ahmet Emre Eskazan
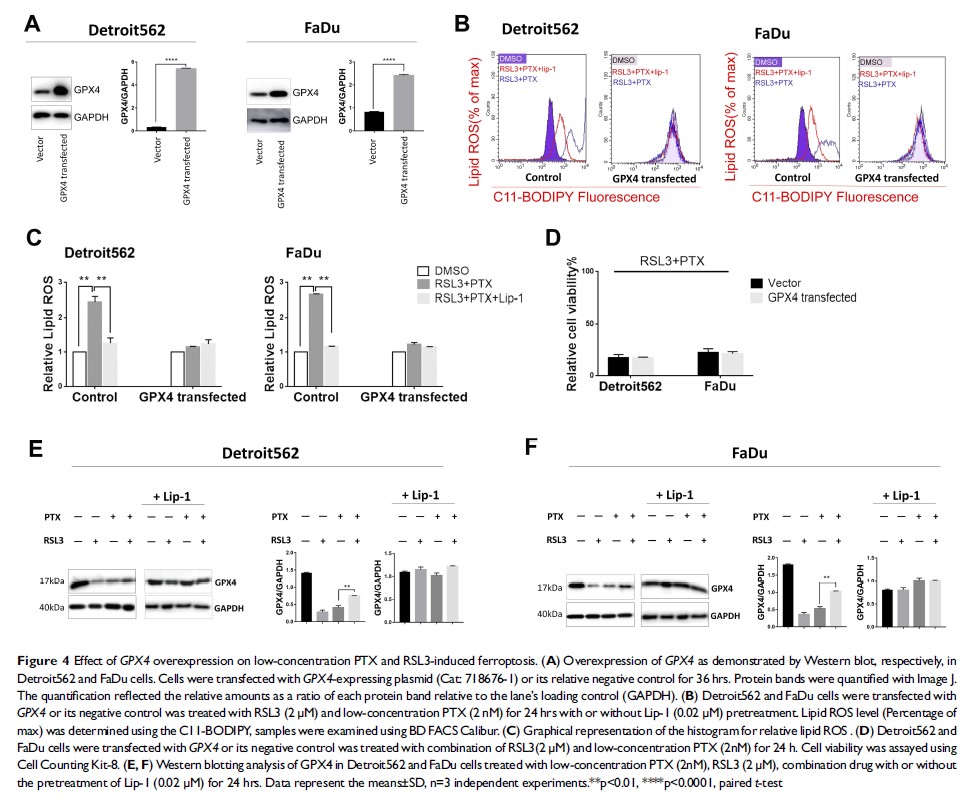
Introduction: RSL3-induced ferroptosis is a cell death pathway dependent upon intracellular iron and is characterized by accumulation of lipid hydroperoxides. Glutaminolysis, a glutamine-fueled intracellular metabolic pathway, is an essential pathway of ferroptosis in cancer cells. Recent findings showed low-concentration paclitaxel (PTX) could inhibit cell death by upregulating p53 expression; downregulating glutaminolysis-related genes.
Methods: The therapeutic effect of RSL3 plus low-concentration PTX combination therapy was investigated in HPSCC cells harboring mutant p53 (mtp53 ). Relative cell viability, ferroptosis-specific lipid peroxidation and relevant protein expression were evaluated.
Results: We demonstrated that neither PTX nor RSL3 in low concentration caused significant cell death; however, the combination therapy is shown to induce ferroptosis and significant cell death in mtp53 HPSCC. We discovered that low-concentration PTX enhanced the RSL3-induced ferroptosis by upregulating mtp53 expression. Furthermore, mtp53 -mediated transcriptional regulation of SLC7A11 could be the key determinant.
Discussion: Although gain-of-function of p53 variants remains to be characterized, our findings provide new insight into the synergistical cell death by regulating ferroptosis and p53 .
Keywords: HPSCC, ferroptosis, low-concentration paclitaxel, RSL3, synthetic cell death, mtp53, SLC7A11, GOF p53 variants