111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

circ-MYBL2 作为 miR-361-3p 的海绵,可促进宫颈癌细胞的增殖和侵袭
Authors Wang J, Li H, Liang Z
Received 10 June 2019
Accepted for publication 13 September 2019
Published 20 November 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 9957—9964
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S218976
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Aruna Narula
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Arseniy Yuzhalin
Background: Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have been considered as a key regulator in tumor carcinogenesis. However, the roles and underlying mechanisms of circRNAs in cervical cancer (CC) remain largely unknown. In this study, we explored the effects of circ-MYBL2 (hsa_circ_0060467) on CC progression.
Methods: Levels of circ-MYBL2 and miR-361-3p were examined by qRT-PCR. CCK-8 assay, colony formation assay and transwell invasion assay were used to determine the roles of circ-MYBL2 in CC. Dual-luciferase reporter and RNA pull down assays were employed to verify the relationship between circ-MYBL2 and miR-361-3p.
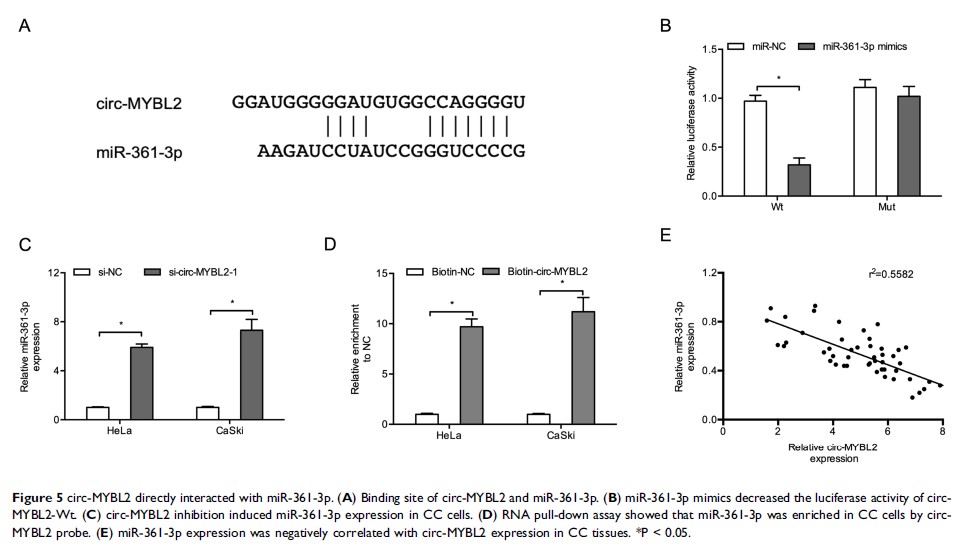
Results: We showed that the expression of circ-MYBL2 was significantly upregulated and positively associated with advanced FIGO stage, larger tumor size, lymph node metastasis, and poor prognosis in CC patients. Function assays revealed that circ-MYBL2 inhibition suppressed CC cells’ proliferation, invasion and epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) processes. In mechanism, miR-361-3p was identified as a direct target of circ-MYBL2, rescue assays showed that miR-361-3p suppression reversed the effects of si-circ-MYBL2 on CC cells’ progression.
Conclusion: Our findings suggested that circ-MYBL2 promoted CC progression by regulating miR-361-3p expression, which provided a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of CC patients.
Keywords: circ-MYBL2, miR-361-3p, cervical cancer, proliferation, invasion