111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过综合分析确定高级别浆液性卵巢癌的分子生物标志物
Authors Si M, Zhang J, Cao J, Xie Z, Shu S, Zhu Y, Lang J
Received 26 August 2019
Accepted for publication 30 October 2019
Published 21 November 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 10057—10075
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S228678
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Aruna Narula
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos E Vigil
Purpose: Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of gynecologic cancer-related death worldwide. Early diagnosis of ovarian cancer can significantly improve patient prognosis. Hence, there is an urgent need to identify key diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers specific for ovarian cancer. Because high-grade serous ovarian cancer (HGSOC) is the most common type of ovarian cancer and accounts for the majority of deaths, we identified potential biomarkers for the early diagnosis and prognosis of HGSOC.
Methods: Six datasets (GSE14001, GSE18520, GSE26712, GSE27651, GSE40595, and GSE54388) were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus database for analysis. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between HGSOC and normal ovarian surface epithelium samples were screened via integrated analysis. Hub genes were identified by analyzing protein–protein interaction (PPI) network data. The online Kaplan-Meier plotter was utilized to evaluate the prognostic roles of these hub genes. The expression of these hub genes was confirmed with Oncomine datasets and validated by quantitative real-time PCR and Western blotting.
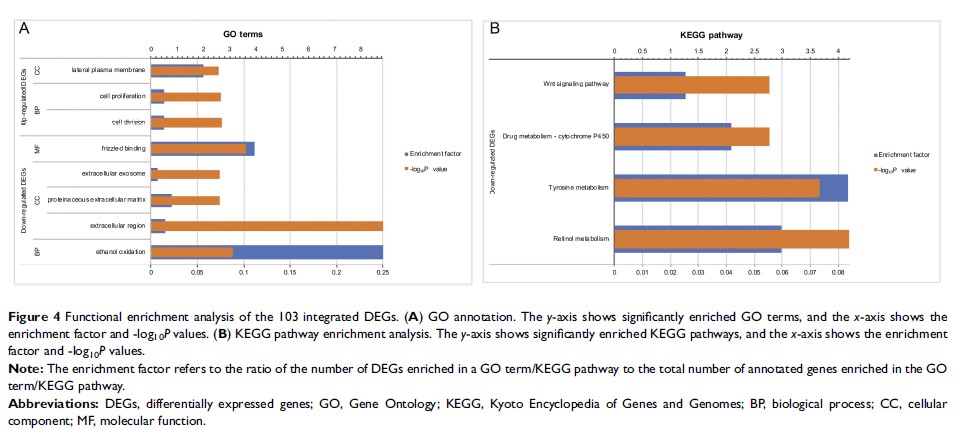
Results: A total of 103 DEGs in patients with HGSOC—28 upregulated genes and 75 downregulated genes—were successfully screened. Enrichment analyses revealed that the upregulated genes were enriched in cell division and cell proliferation and that the downregulated genes mainly participated in the Wnt signaling pathway and various metabolic processes. Ten hub genes were associated with HGSOC pathogenesis. Seven overexpressed hub genes were partitioned into module 1 of the PPI network, which was enriched in the cell cycle and DNA replication pathways. Survival analysis revealed that MELK, CEP55 and KDR expression levels were significantly correlated with the overall survival of HGSOC patients (P < 0.05). The RNA and protein expression levels of these hub genes were validated experimentally.
Conclusion: Based on an integrated analysis, we propose the further investigation of MELK, CEP55 and KDR as promising diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers of HGSOC.
Keywords: high-grade serous ovarian cancer, integrated analysis, bioinformatic analysis, differentially expressed genes, survival, biomarker