111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

c-Jun 和 HOTAIR 的相互作用及 p21 的表达增加在多叶素I抑制人肺癌细胞生长中发挥综合作用
Authors Zhao Y, Tang X, Huang Y, Tang Q, Ma C, Zheng F, Wu W, Hann SS
Received 11 August 2019
Accepted for publication 31 October 2019
Published 25 November 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 10115—10127
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S226830
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Rachel Predeepa
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
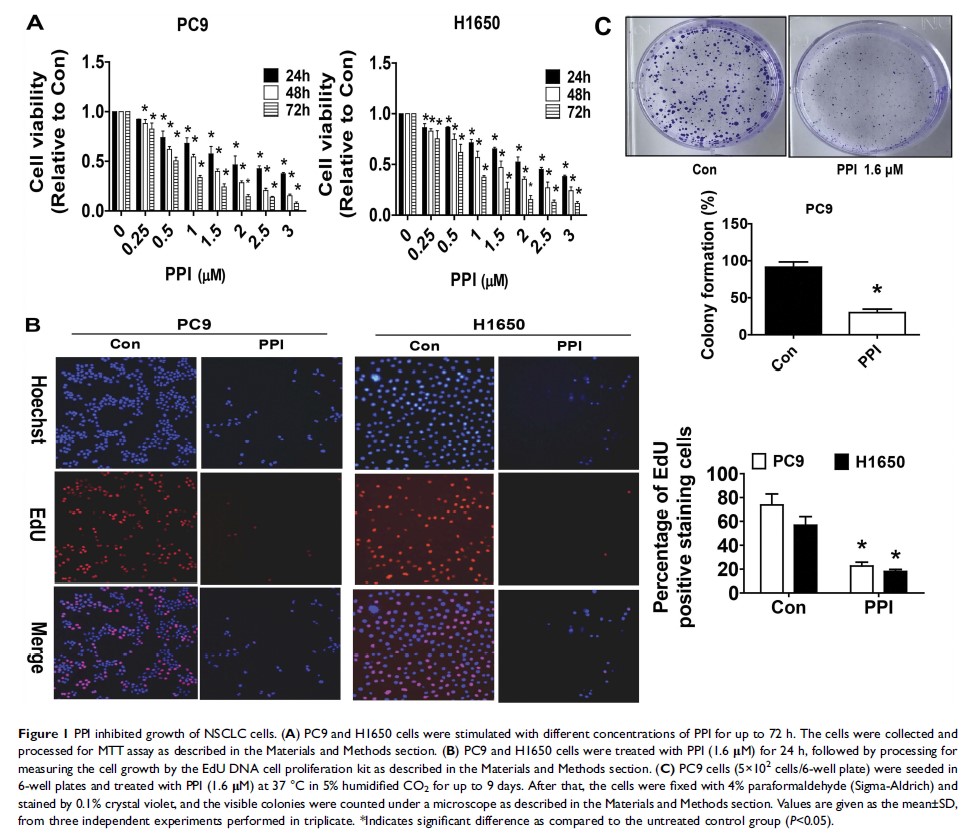
Background: Lung cancer is a leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Previously we demonstrated that polyphyllin I (PPI), a bioactive component extracted from Paris polyphylla, inhibited the growth of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells through the SAPK/JNK-mediated suppressing p65, DNMT1 and EZH2 expressions. However, the molecular mechanism underlying anti-lung cancer effect by PPI still remain elusive.
Purpose: In this current study, we further explored the molecular mechanism underlying the anti-lung cancer effect of PPI.
Methods: MTT, Cell-LightTM EdU DNA cell proliferation and colony formation assays were used to measure cell growth. Western blot were used to examine protein levels of c-Jun and p21. The expression level of long non-codingth RNA HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) was measured by qRT-PCR. The p21 promoter activity was measured by Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay System. The transient transfection experiments were used to silence and overexpression of c-Jun, p21 and HOTAIR. Tumor xenograft and bioluminescent imaging experiments were carried out to confirm the in vitro findings.
Results: We showed that PPI suppressed growth of NSCLC cells. Mechanistically, we observed that PPI reduced expression of HOTAIR, while increased transcription factor c-Jun protein levels. Additionally, PPI also induced protein expression and promoter activity of p21, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor. While exogenously expressed HOTAIR showed no effect on c-Jun levels, silencing of c-Jun significantly reversed the PPI-inhibited HOTAIR expression. Moreover, excessive expressed c-Jun further enhanced PPI-inhibited HOTAIR expression and PPI-induced p21 protein levels. Intriguingly, overexpression of HOTAIR and silencing of c-Jun overcame the PPI-induced p21 protein and promoter activity. Finally, silencing of p21 neutralized the PPI-inhibited cell proliferation. Similar results were also found in one xenograft mouse model.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate that PPI inhibits growth of NSCLC cells through regulation of HOTAIR and c-Jun expressions, which lead to induction of p21 gene. The interactions among HOTAIR, c-Jun and p21 regulatory axis converge in the overall anti-lung cancer effect of PPI. This study unveils an additional new mechanism for the anti-lung cancer role of PPI.
Keywords: PPI, NSCLC, HOTAIR, c-Jun, p21