111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

ENO1 充当预后生物标志物候选者,并通过调节 Rab1A 在大肠癌中的表达提高肿瘤的生长和迁移能力
Authors Cheng Z, Shao X, Xu M, Zhou C, Wang J
Received 7 August 2019
Accepted for publication 30 October 2019
Published 26 November 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 9969—9978
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S226429
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Background: Colorectal carcinoma (CRC) is one of the most common malignancies with a dismal 5‐year survival rate. The glycolytic enzyme α-enolase (ENO1 ) is overexpressed in multiple cancers and is involved in tumor cell proliferation and metastasis. However, its clinical significance, biological role, and underlying molecular mechanisms in CRC are still unclear. The aim of the present study was to investigate the potential role of ENO1 in the initiation and development of CRC.
Patients and methods: The in situ expression of ENO1 in CRC and adjacent normal tissues was examined by immunohistochemistry. The effects of ENO1 on the in vitro proliferation and migration of CRC cell lines were investigated by MTT, colony formation, and Transwell assays. Finally, the in vivo tumorigenic capacity of ENO1 was assessed in a mouse model.
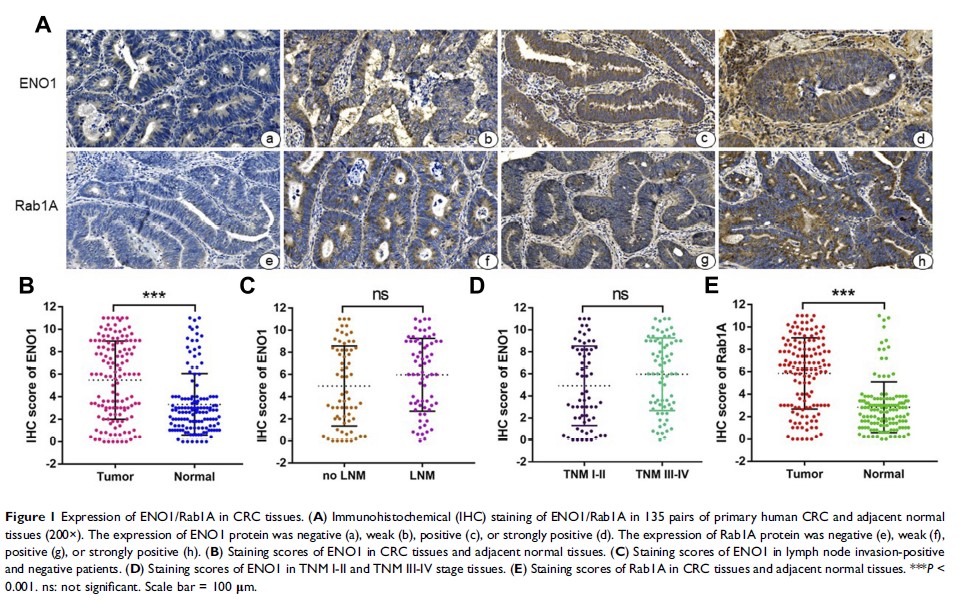
Results: ENO1 was overexpressed in CRC tissues and significantly correlated with the clinicopathological parameters. Furthermore, Rab1A was also overexpressed in CRC tissues and was positively correlated to that of ENO1. The high expression levels of both ENO1 and Rab1A led to significantly worse prognosis of CRC patients compared to either alone. Furthermore, knockdown of ENO1 significantly inhibited CRC cells proliferation and migration in vitro and reduced xenograft growth in vivo via the concomitant downregulation of Rab1A.
Conclusion: The ENO1/Rab1A signaling axis is involved in CRC progression and is a potential biomarker for the treatment of CRC.
Keywords: colorectal cancer, ENO1 , Rab1A , prognosis, tumor growth