111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

确定用于 HBV 相关性肝细胞癌检测的新型 lncRNA
Authors Li Y, Chen X, Huang H, Li G, Liao L, Yuan T, Deng S
Received 9 September 2019
Accepted for publication 2 November 2019
Published 27 November 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 10199—10211
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S230377
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Mr Davin Leif
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos E Vigil
Purpose: This study was conducted to investigate the differentially expressed profiles of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in HBV-associated HCC (HBV-HCC), which may serve as potential diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
Methods: To examine the differentially expressed profiles of lncRNAs and mRNAs using microarray analysis, we collected 15 specimens: five HBV-associated HCC tissues, five paired adjacent peritumoral liver tissues (APLT), and five distant peritumoral liver tissues (DPLT). Then, Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analyses were performed to predict the biological roles and potential signaling pathways of these dysregulated mRNAs. In addition, lncRNA-mRNA co-expression network and signal transduction pathway network (Signal-net) were employed to further explore the potential target genes and roles of dysregulated lncRNAs in HBV-HCC pathogenesis. Finally, quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was used to confirm the expression of six selected dysregulated lncRNAs.
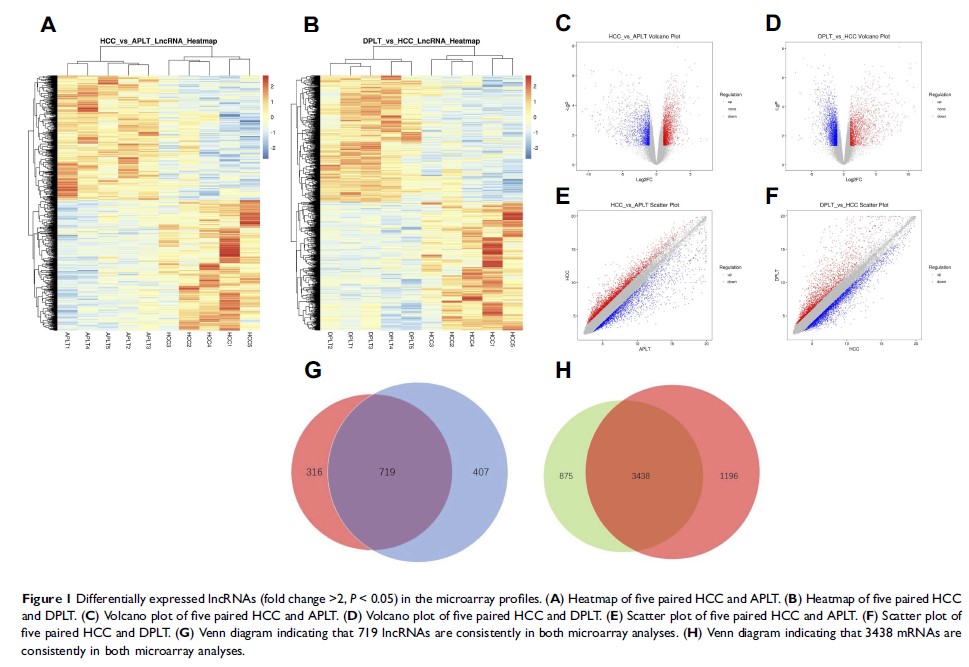
Results: A total number of 719 lncRNAs and 3438 mRNAs were significantly more dysregulated in HBV-HCC tissues than in APLT and DPLT (fold change > 2, P < 0.05, FDR < 0.05). Additionally, 337 GO terms and 53 KEGG pathways were established to be significantly enriched. These dysregulated mRNAs were mainly enriched in metabolism-related biological processes. Additionally, lncRNA-mRNA coexpression network analysis showed that NONHSAT053785 is at the core of the network. Furthermore, the Signal-net analysis showed that CYP3A4 was gene with the highest degree. Finally, the data of five of the six selected differentially expressed lncRNAs were in agreement with the microarray data obtained by qRT-PCR verification.
Conclusion: Our study revealed the differentially expressed profiles of lncRNAs and mRNAs for HBV-HCC, and five novel dysregulated lncRNAs were identified in HBV-HCC tissues. The aforementioned dysregulated lncRNAs may represent potential diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets of HBV-HCC, which needs to be validated in future studies.
Keywords: long non-coding RNA, hepatocellular carcinoma, microarray, biomarker