111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

贝伐单抗联合培美曲塞和铂类药物可显着改善晚期非小细胞肺癌腺癌和脑转移患者的临床疗效
Authors Tian Y, Zhai X, Tian H, Jing W, Zhu H, Yu J
Received 12 July 2019
Accepted for publication 14 November 2019
Published 29 November 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 10083—10092
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S222910
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Nakshatri
Background: The study aims to evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of bevacizumab in combination with the first-line pemetrexed-platinum (PP) in patients with advanced adenocarcinoma non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and brain metastases.
Methods: The clinical data of patients with adenocarcinoma NSCLC and symptomatic or asymptomatic brain metastases were collected in our study. The basic chemotherapy regimen was pemetrexed-platinum (PP). According to whether combined with bevacizumab (B) or not, all enrolled patients were assigned to the B+PP group or the PP alone group.
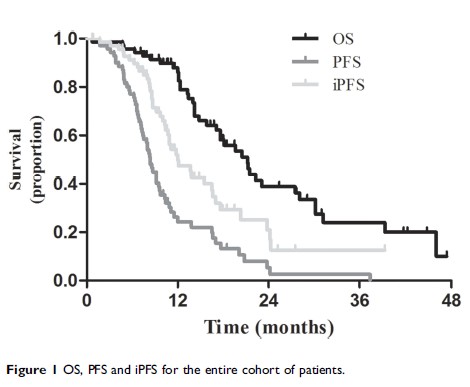
Results: A total of 71 patients were enrolled in the current study. Twenty-six patients were allocated to the B+PP group and 45 were allocated to the PP group. Overall response rates (ORRs), disease control rates (DCRs) of the thoracic tumors and intracranial metastases and overall survival (OS) were not significantly different between the 2 groups. However, progression-free survival (PFS) and intracranial PFS (iPFS) were significantly prolonged in the B+PP group compared with the PP group. The median PFS was 9.2 and 8.2 months, and the 1-year PFS rates were 47.1% and 15.9%, respectively, in the 2 groups (P =0.029). And, the median iPFS were 24.3 and 10.9 months, and the 1-year iPFS rates were 80.1% and 40.1%, respectively, in the 2 groups (P =0.008). Univariate and multivariate analyses suggested that maintenance therapy and bevacizumab therapy were independent favorable prognostic factors of PFS and iPFS.
Conclusion: The addition of bevacizumab to the first-line pemetrexed and platinum significantly improved clinical outcomes of patients with advanced adenocarcinoma NSCLC and brain metastases.
Keywords: bevacizumab, non-small cell lung cancer, brain metastases, clinical outcome, toxicity