111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

HPV 16 的重组病毒衣壳蛋白 L2(rVL2)通过 ITGB7/C/EBPβ 信号通路抑制宫颈癌细胞系中的细胞增殖和葡萄糖代谢
Authors Chai Z, Yang Y, Gu Z, Cai X, Ye W, Kong L, Qiu X, Ying L, Wang Z, Wang L
Received 25 August 2019
Accepted for publication 11 November 2019
Published 29 November 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 10415—10425
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S228631
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Sushma Chaurasia
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
Purpose: Capsid protein L2 is the minor capsid protein of human papillomavirus 16 (HPV16). Although L2-based vaccines were developed, the therapeutic effect of recombinant viral capsid protein L2 (rVL2) was still to be illustrated.
Methods: We used glucose uptake and lactate production assay to verify the inhibitory effect of rVL2 on the glucose metabolism in cervical cancer cells. Secondly, we performed gene-chip assay, RT-PCR, and Western blot to determine the role of ITGB7/C/EBPβ signaling pathway in rVL2-mediated glucose metabolism in vitro. Finally, we used an animal model to verify the function of rVL2 in cervical cancer.
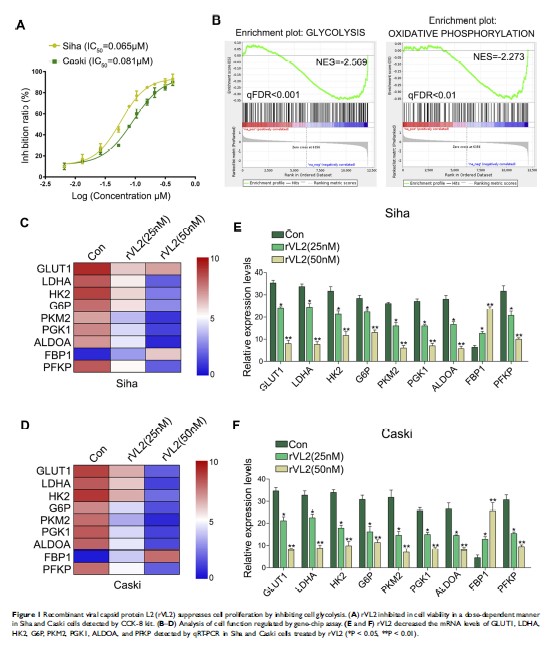
Results: We found that rVL2 reduced glucose uptake and lactate production levels in cervical cancer cells, which caused the inhibition of cell proliferation. rVL2 decreased the expression levels of key metabolic enzymes, including GLUT1, LDHA, and ALDOA, to affect cell metabolism in cervical cancer cells by inhibiting ITGB7/C/EBPβ signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusion: These results demonstrated the vital role of rVL2 in the glycolysis-induced cell growth and proliferation via suppressing ITGB7/C/EBPβ signaling axis.
Keywords: recombinant viral capsid protein L2, rVL2, C/EBPβ, glucose metabolism, cervical cancer