111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

对癌症风险人群而言,早期肝细胞癌射频消融、手术切除和移植的比较疗效:倾向评分加权分析的结果
Authors Zhao WJ, Zhu GQ, Wu YM, Wang WW, Bai BL
Received 26 July 2019
Accepted for publication 14 November 2019
Published 29 November 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 10389—10400
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S224809
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Aruna Narula
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Arseniy Yuzhalin
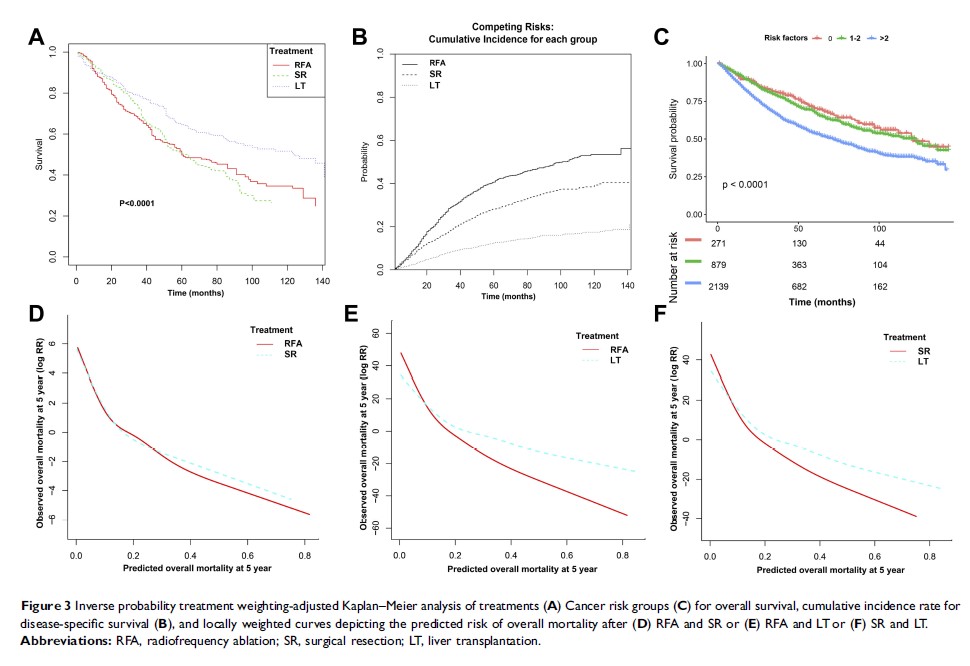
Purpose: Controversies exist for which treatment is optimal for early hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): radiofrequency ablation (RFA), surgical resection (SR), or transplantation (LT). We compared outcomes between treatments as first-line therapy for HCC patients measuring up to 5 cm or different cancer risk groups.
Patients and methods: The Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database was retrieved for HCC patients treated with RFA, SR, or LT between 2004 and 2015. The effects of three treatments were compared using propensity score, inverse probability of treatment weights adjustment, and instrumental variable analysis for overall survival (OS) and competing risks regression models for disease-specific survival (DSS). We also evaluated whether the effect of treatments varied according to baseline clinical characteristics by locally weighted regression method.
Results: Of 7664 patients, RFA and SR yielded worse OS (HR 1.67, CI 1.43–1.70, P<0.001; HR 1.43, CI 1.40–1.67, P<0.001) and DSS (HR 2.00, CI 1.10–3.30, P<0.011; HR 2.50, CI 2.00–3.30, P<0.001) than LT. In patients with small tumors, SR may confer more survival benefits than RFA (HR>1) for different tumor sizes measuring up to 5 cm and may be an appropriate first-line treatment. Additionally, RFA has more survival benefits compared with SR (HR 0.83, CI 0.53–1.25) for those patients with low tumor risk and good general health condition (without any prognostic risk factors). However, those patients with a predicted 5-year overall mortality risk >30% seem to benefit more for SR than RFA.
Conclusion: Due to a shortage of donors, RFA and SR can be applied as either primary management of HCC or as a bridging therapy for LT. Furthermore, SR is an effective option for patients with different HCC tumor size. However, RFA could achieve comparable survival benefits with SR for patients without any risk factors.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, outcomes, radiofrequency ablation, surgical resection, transplantation, propensity score, PS