111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

雾化吸入布地奈德用于慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重的初始治疗的临床疗效:事后分析
Authors Zheng JP, Zhang J, Ma LJ, Chen P, Huang M, Ou XM, Zhao ZW, Jiang SJ, Cao J, Yao W
Received 30 November 2018
Accepted for publication 12 September 2019
Published 29 November 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 2725—2731
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S196615
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Chunxue Bai
Purpose: The current guidelines recommend the use of systemic corticosteroids (SCS) as the optimal treatment for acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (AECOPD). The aim of this real-world study was to evaluate whether nebulized budesonide (NBS) could also be used as an initial treatment for AECOPD.
Patients and methods: AECOPD patients initially treated with NBS or SCS (oral/intravenous) were enrolled. A large-scale, long-term multicenter cohort study of AECOPD patients was performed to analyze outcomes for each treatment (NCT02051166).
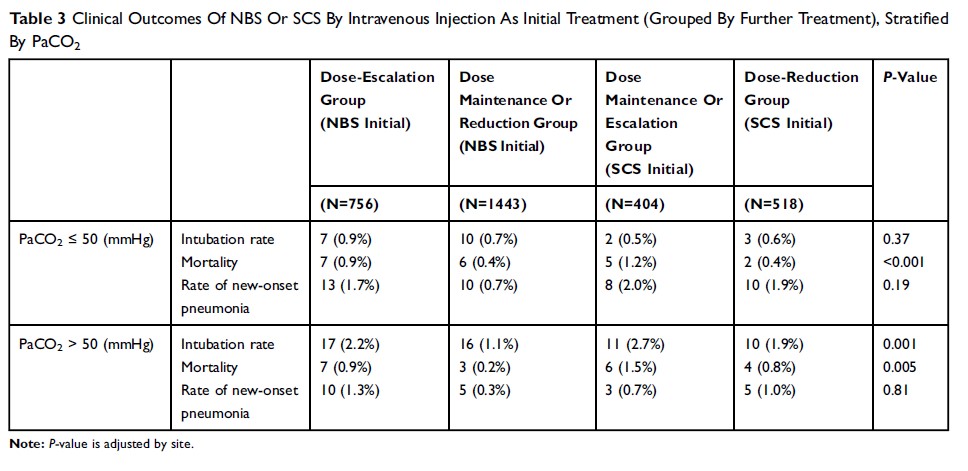
Results: Initial NBS and SCS treatment resulted in similar outcomes in terms of improvements in FEV1, PaO2, SaO2, and PaCO2. Disease severity affected outcome similarly in both groups. When the groups were stratified according to whether the initial treatment was subsequently intensified or reduced, more intubation was seen in the groups in which initial treatment was intensified. NBS escalation and SCS reduction groups spent more days in the hospital. The NBS escalation group was associated with the highest medical expenditure and a relatively higher rate of new-onset pneumonia. The NBS maintenance/reduction group showed the lowest mortality rate between groups. Stratification according to initial PaCO2 level showed more intubation in the groups with high initial PaCO2 concentrations.
Conclusion: These results indicate that NBS may be used as an initial treatment in certain AECOPD patients, and further studies are needed to better define those most likely to benefit.
Keywords: nebulized budesonide, systemic corticosteroids, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, AECOPD