111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

支气管肺泡灌洗液中白细胞介素 27 对肺结核的诊断准确性
Authors Lin S, Wang Y, Li Y, Xiao D, Guo J, Ma W, An W, Liu H, Shi Y, Zhang L, Cui J, Guan W
Received 16 September 2019
Accepted for publication 22 November 2019
Published 2 December 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 3755—3763
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S231215
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Melinda Thomas
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Suresh Antony
Background: The World Health Organization states that China had 0.9 million cases of tuberculosis in 2017, accounting for 9% of cases globally. Despite a decrease in the incidence and mortality of tuberculosis in China over time, development in choosing the appropriate prevention and control of TB is required.
Purpose: The aim of this study was to evaluate the diagnostic significance of interleukin-27 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluids for pulmonary tuberculosis.
Materials and methods: Eventually, 107 bronchoalveolar lavage fluids from patients were included in this study. The concentrations of interleukin-27 and adenosine deaminase were determined in bronchoalveolar lavage fluids using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
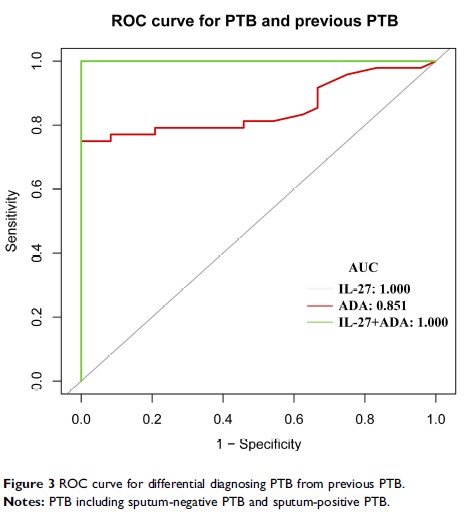
Results: It was found that the concentrations of interleukin-27 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluids of sputum-positive pulmonary tuberculosis group were significantly higher than those in sputum-negative pulmonary tuberculosis, lung cancer, and previous pulmonary tuberculosis groups, respectively (all P <0.001). Interleukin-27 levels in bronchoalveolar lavage fluids could be used for diagnostic purpose for pulmonary tuberculosis, with the cutoff value of 7.867 pg/mL; interleukin-27 had a sensitivity of 68.8% and specificity of 100% for the differential diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis (sputum-negative and sputum-positive PTB) from lung cancer. And with the cutoff value of 6.012 pg/mL, IL-27 had sensitivity and specificity of both 100% for the differential diagnosis of PTB from previous PTB. The risk of pulmonary tuberculosis was positively associated with the concentrations of interleukin-27 and adenosine deaminase in bronchoalveolar lavage fluids.
Conclusion: Interleukin-27 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluids is a sensitive and specific biomarker for the differential diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis from lung cancer and previous pulmonary tuberculosis.
Keywords: pulmonary tuberculosis, interleukin-27, adenosine deaminase, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid