111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

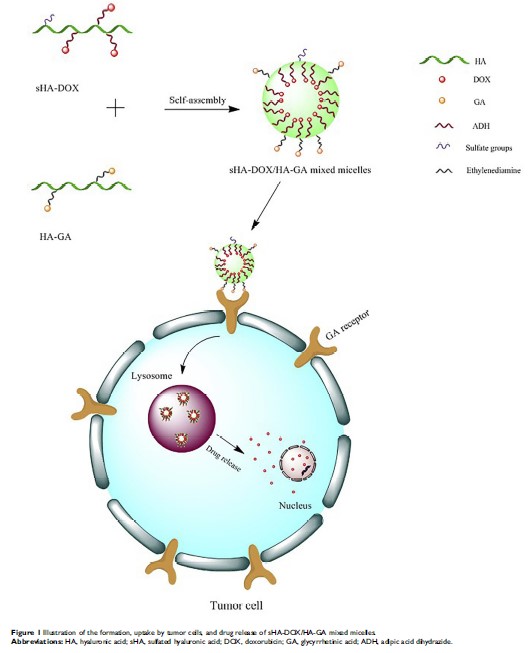
肝靶向性和 pH 敏感的硫酸化透明质酸混合胶束用于肝癌治疗
Authors Li Z, Tian G, Jiang H, Pan R, Lian B, Wang M, Gao Z, Zhang B, Wu J
Received 5 May 2019
Accepted for publication 8 November 2019
Published 2 December 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 9437—9452
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S214528
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Melinda Thomas
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Background: The tumor-targeting ability and pH-sensitive properties of intelligent drug delivery systems are crucial for effective drug delivery and anti-tumor therapy.
Methods: In this study, sHA-DOX/HA-GA mixed micelles were designed with the following properties: sulfated hyaluronic acid (sHA) was synthesized to block cell migration by inhibiting HAase; sHA-DOX conjugates were synthesized via pH-sensitive hydrazone bond to realize DOX-sensitive release. The introduction of HA-GA conjugate could improve active-targeting ability and cellular uptake.
Results: The results showed that the mixed micelles possessed a nearly spherical shape, nanoscale particle size (217.70±0.89 nm), narrow size distribution (PDI=0.07±0.04), negative zeta potential (−31.87±0.61 mV) and pH-dependent DOX release. In addition, the sHA-DOX/HA-GA micelles exhibited concentration-dependent cytotoxicities against liver carcinoma cells (HepG2) and HeLa cells, and were shown to be effectively taken up by HepG2 cells by confocal microscopy analysis. Furthermore, the in vivo anti-tumor study showed that mixed micelles had a superior anti-tumor effect compared to that of free DOX. Further evidence obtained from the hematoxylin–eosin staining and immunohistochemistry analysis also demonstrated that sHA-DOX/HA-GA exhibited stronger tumor inhibition and lower systemic toxicity than free DOX.
Conclusion: The sHA-DOX/HA-GA mixed micelles could be a potential drug delivery system for anti-hepatoma therapy.
Keywords: hyaluronic acid, glycyrrhetinic acid, hepatoma-targeting, pH-sensitive, micelles, anti-tumor therapy