111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

CircCDYL 作为套细胞淋巴瘤中的新生物标记物并促进细胞增殖
Authors Mei M, Wang Y, Wang Q, Liu Y, Song W, Zhang M
Received 23 September 2019
Accepted for publication 15 November 2019
Published 3 December 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 10215—10221
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S232075
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Shreya Arora
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eileen O'Reilly
Introduction: Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is a rare subtype of B-cell lymphoma. Circular (circ) RNA is a member of the non-coding RNA family. However, clinical references to circRNAs in MCL are not clear.
Methods: In this study, we detected the expression level of circCDYL in the plasma of MCL patients compared to healthy donors by the quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. The diagnostic value of circCDYL was determined using a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. We constructed a circCDYL short hairpin RNA plasmid and infected the MCL cell line, Z138, to detect its effect on cell proliferation.
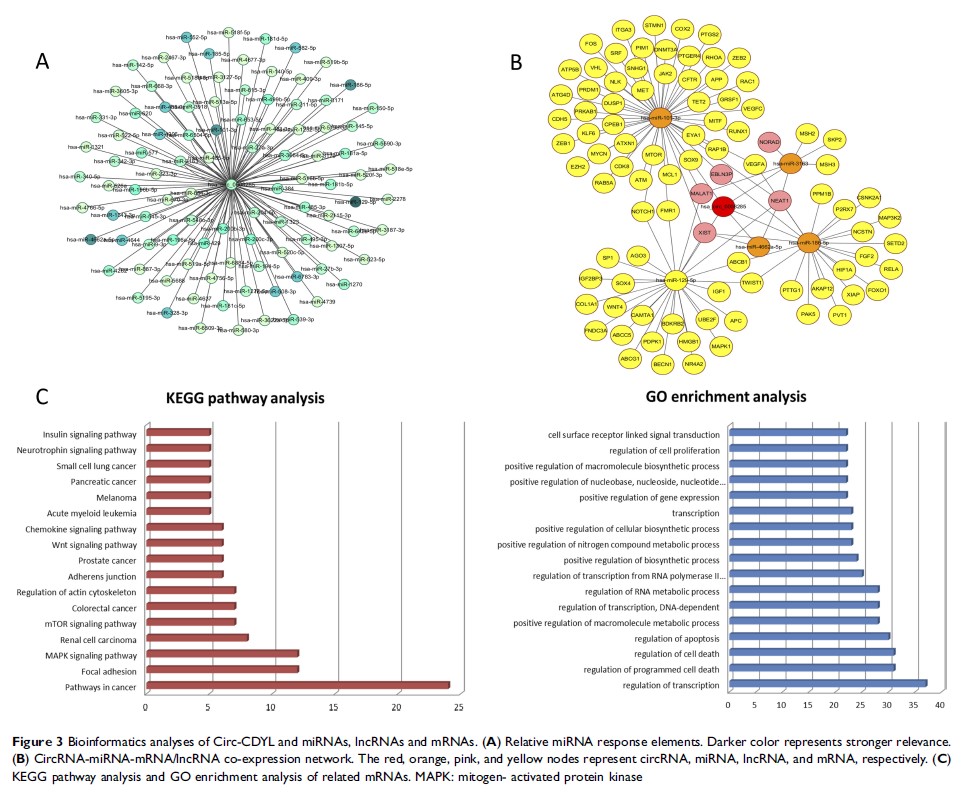
Results: CircCDYL was high expressed in the plasma of MCL patients. The ROC curve showed that circCDYL had diagnostic value (area under the curve (AUC) = 0.856). Functionally, circCDYL knockdown inhibited MCL cell proliferation. We conducted bioinformatics analyses and identified a circCDYL-micro (mi)RNA–mRNA/long non-coding (lnc)RNA network, highlighted by five miRNAs (hsa-miR-129-5p, hsa-miR-3163, hsa-miR-4662a-5p, hsa-miR-101-3p, and hsa-miR-186-5p), three lncRNAs (MALAT1, NEAT1, and XIST), and five mRNAs (NOTCH1, FMR1, ABCB1, TWIST1, and VEGFA).
Conclusion: These findings indicate that circ-CDYL might serve as a potential diagnostic biomarker in clinical practice.
Keywords: circular RNA, biomarker, AUC, diagnosis, non-coding RNA