111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

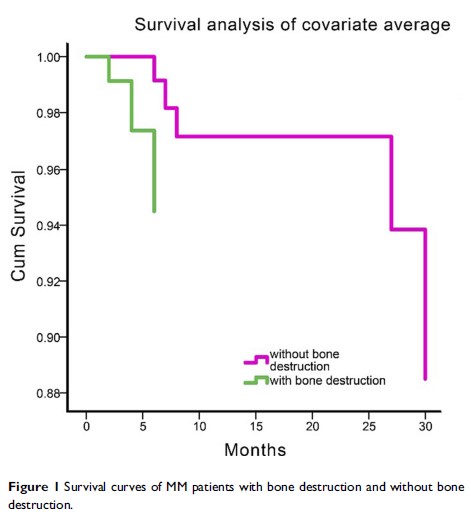
回顾性分析:预测 419 例新诊断的多发性骨髓瘤的骨破坏生存率和风险分层的一个新指数
Authors Jin Y, Shang Y, Liu H, Ding L, Tong X, Tu H, Yuan G, Zhou F
Received 29 August 2019
Accepted for publication 22 October 2019
Published 3 December 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 10587—10596
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S229122
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Isha Chandra
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
Objective: Multiple myeloma (MM) patients with bone destruction are difficult to restore, so it is of great clinical significance to further explore the factors affecting MM bone destruction.
Methods and results: This study retrospectively analyzed 419 cases with MM. Multiple linear regression analysis showed that those MM patients with a higher concentration of Ca2+ in serum, higher positive rate of CD138 immuno-phenotype and advanced in stage with 13q34 deletion in cytogenetics would be more prone to bone destruction, while total bile acid (TBA) and kappa chain isotope negatively correlated with bone destruction in MM patients. The Kaplan–Meier analysis indicated that Ca2+, serum β2-microglobulin (β2-MG), hemoglobin (HGB), creatinine (CREA), uric acid (UA) and age correlated with the survival of bone destruction in MM patients. Cox regression analysis further showed that the independent prognostic factors of β2-MG and CREA had a higher risk for early mortality in bone destruction patients. Moreover, an index was calculated based on β2-MG and globulin (GLB) to white blood cell (WBC) ratio to predict the poor survival of bone destruction patients.
Conclusion: We provide a novel marker to predict the prognosis of myeloma patients using routine examination method instead of bone marrow aspiration, and provide a reference for clinical evaluation.
Keywords: multiple myeloma, bone destruction, prediction index, prognosis