111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

哪种移动健康应用程序是患者最想要的?对多名门诊手术患者的初步研究
Authors Tang MY, Li ZC, Dai Y, Li XL
Received 20 June 2019
Accepted for publication 16 October 2019
Published 4 December 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 2039—2046
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S220207
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Naifeng Liu
Background: An increasing number of surgeries are performed as ambulatory surgeries, and mobile health applications (m-health apps) have therefore been designed to help provide patients with more convenient health-care services and improve the working efficiency of health-care professionals (HCPs). To find an effective approach to design such m-health apps, a study to evaluate ambulatory surgery patients’ preferences is necessary.
Methods: A structured questionnaire was distributed to 360 patients undergoing ambulatory surgery to understand their demographic characteristics, preferences regarding the features and functions of m-health apps and willingness to engage with m-health apps.
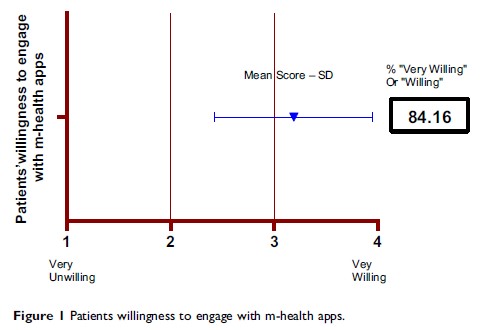
Results: In total, 84.16% of ambulatory surgery patients stated that they would be willing to engage with an m-health app during the perioperative period. In addition, their top 10 necessary features and functions of m-health apps were related mainly to ambulatory surgery and communication with HCPs. Furthermore, younger age (χ 2=10.42, p <0.01), employment (χ 2=9.04, p <0.01), higher education (χ 2=13.67, p <0.01), longer daily use of phones (χ 2=11.84, p <0.01) and more frequent usage of m-health apps (χ 2=23.23, p <0.01) were associated with patients’ willingness to engage with m-health apps, but only more frequent usage of m-health apps (OR=2.97, 95% CI=1.54–5.71, p <0.01) was found to be a predictor.
Conclusion: This study presents an initial evaluation of ambulatory surgery patients’ preferences regarding m-health apps. Gaining these insights will be useful to help us design an evidence-based, highly functional m-health app that best meets the needs of patients undergoing ambulatory surgery.
Keywords: mobile health applications, ambulatory surgery, preferences