111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

氯化钴通过 HIF-1α/c-Myc 轴抑制 GPC3 在 HepG2 细胞中的表达,从而诱导细胞凋亡
Authors Tong Y, Tong K, Zhu Q, Wu Y, Yang Y, Zhang J, Hu P, Yan S
Received 14 August 2019
Accepted for publication 15 November 2019
Published 5 December 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 10663—10670
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S227215
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Nicola Silvestris
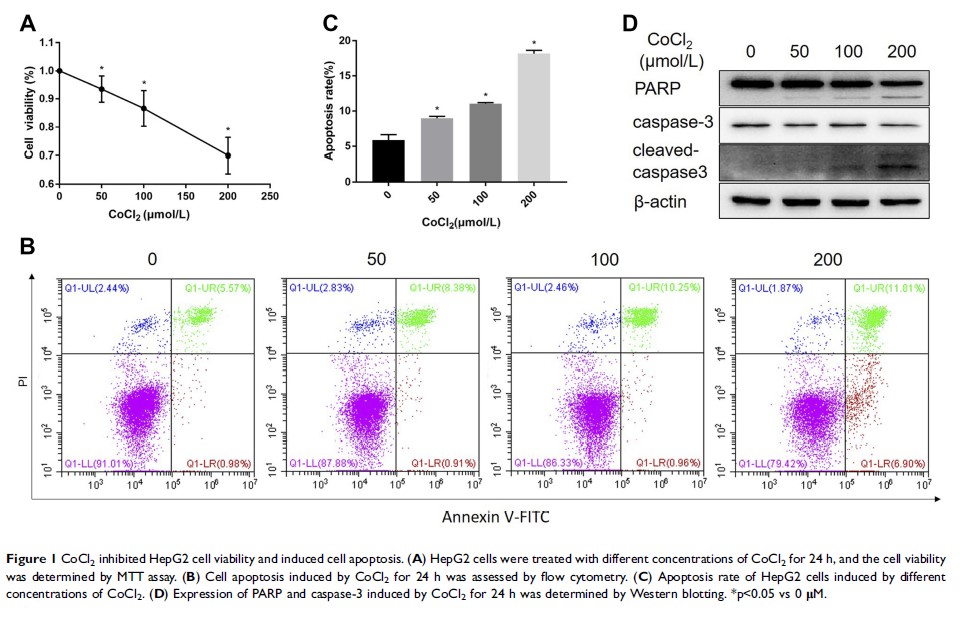
Purpose: To investigate the role of glypican-3 (GPC3) in cobalt chloride (CoCl2)-induced cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Methods: HepG2 cells were treated with CoCl2 in the absence or presence of GPC3 plasmid transfection. Cell viability and apoptosis were assessed by MTT assay and flow cytometry, respectively. The expression of GPC3, hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α), c-myc, sp1, poly-ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) and caspase-3 was determined by real-time PCR, Western blotting, and immunofluorescence after the cells were treated with different concentrations of CoCl2 or siRNA targeting HIF-1α.
Results: CoCl2 significantly inhibited the proliferation of HepG2 cells and induced apoptosis. Additionally, the expression of GPC3 mRNA and protein was decreased, and overexpression of GPC3 attenuated the tumour inhibiting effects. Further studies showed that CoCl2 increased the expression of HIF-1α while reducing the expression of sp1 and c-myc; knockdown of HIF-1α elevated the expression of GPC3, sp1, and c-myc.
Conclusion: CoCl2 inhibited the growth of HepG2 cells through downregulation of GPC3 expression via the HIF-1α/c-myc axis.
Keywords: cobalt chloride, c-myc, glypican-3, hepatocellular carcinoma, hypoxia-inducible factor 1α