111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

较长的非编码 RNA HULC 通过使 miR-6754-5p 海绵化来调节 LYPD1 表达,从而促进乳腺癌的发展
Authors Wang N, Zhong C, Fu M, Li L, Wang F, Lv P, Zhu M, Xiong Y, Mi H, Gu Y
Received 5 August 2019
Accepted for publication 15 November 2019
Published 5 December 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 10671—10679
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S226040
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Shashank Kaushik (PT)
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
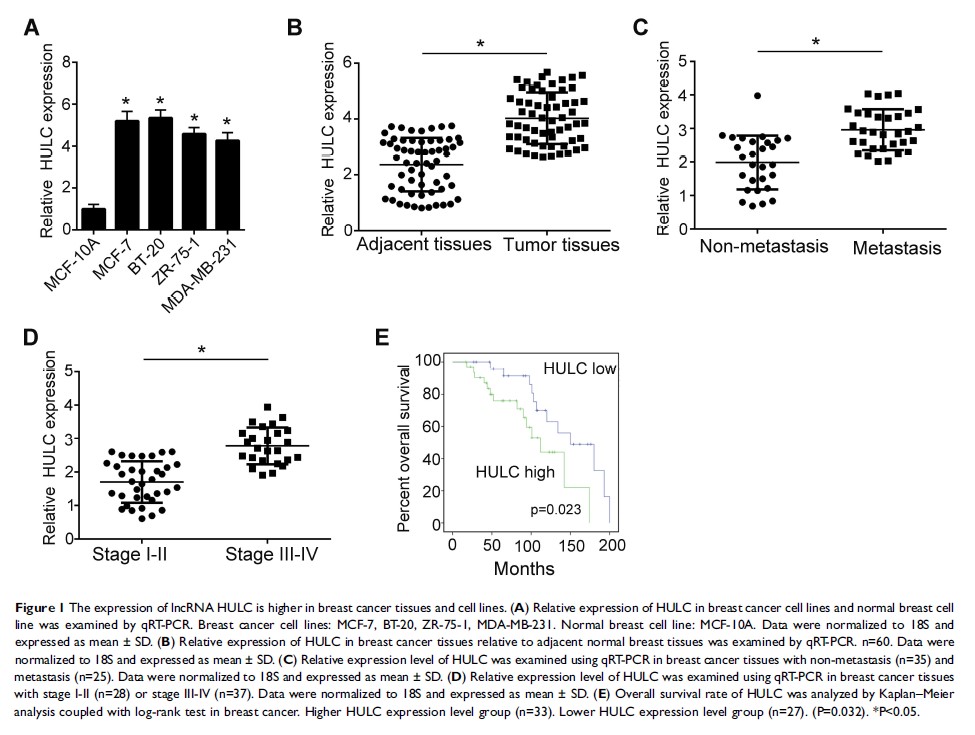
Introduction: Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) were found to regulate many biological processes including cancer development, immunology and other diseases. LncRNA HULC was found to be oncogenes in many cancer progression. However, the role of HULC in the regulation of breast cancer remains unclear.
Methods: The expression of HULC and miR-6754-5p was examined by RT-PCR. Through knockdown of HULC, we found that the proliferation abilities coupled with migration and invasion abilities were significantly decreased. And also, we verified that overexpression of miR-6754-5p significantly decreased the proliferation ability of breast cancer cells.
Results: In this study, we found that lncRNA HULC was overexpressed in breast cancer tissues and cell lines compared to normal healthy breast tissues and normal breast cell line. Moreover, the high expression of HULC was associated with metastasis and malignancy of breast cancers. Mechanically, we found that HULC can bind to miR-6754-5p directly through complementary base pairing. Furthermore, we found that HULC regulates the expression of LYPD1 through sponging miR-6754-5p. Moreover, overexpression of LYPD1 can rescue the migration and invasion abilities of breast cancer cells decreased by knockdown of HULC or overexpression of miR-6754-5p.
Conclusion: Our study showed the role of HULC in promoting breast cancer development and explained the detailed molecular mechanisms.
Keywords: lncRNA HULC, breast cancer development, miR-6754-5p, LYPD1