111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

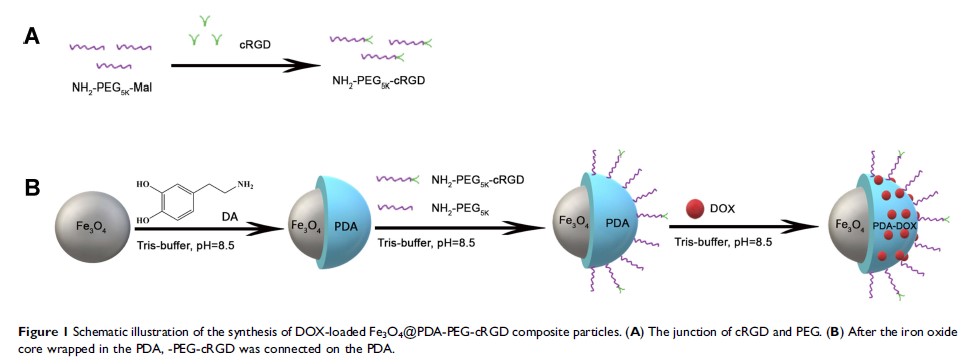
cRGD-偶联 Fe3O4@PDA-DOX 多功能纳米复合材料,用于 MRI 和抗肿瘤化学光热疗法
Authors Fan X, Yuan Z, Shou C, Fan G, Wang H, Gao F, Rui Y, Xu K, Yin P
Received 11 July 2019
Accepted for publication 7 November 2019
Published 5 December 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 9631—9645
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S222797
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: Photothermal therapy (PTT) has great potential in the clinical treatment of tumors. However, most photothermal materials are difficult to apply due to their insufficient photothermal conversion efficiencies (PCEs), poor photostabilities and short circulation times. Furthermore, tumor recurrence is likely to occur using PTT only. In the present study, we prepared cyclo (Arg-Gly-Asp-d-Phe-Cys) [c(RGD)] conjugated doxorubicin (DOX)-loaded Fe3O4@polydopamine (PDA) nanoparticles to develop a multifunctional-targeted nanocomplex for integrated tumor diagnosis and treatment.
Materials and methods: Cytotoxicity of Fe3O4@PDA-PEG-cRGD-DOX against HCT-116 cells was determined by cck-8 assay. Cellular uptake was measured by confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM). Pharmacokinetic performance of DOX was evaluated to compare the differences between free DOX and DOX in nanocarrier. Performance in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and antitumor activity of complex nanoparticles were evaluated in tumor-bearing nude mice.
Results: Fe3O4@PDA-PEG-cRGD-DOX has a particle size of 200–300 nm and a zeta potential of 22.7 mV. Further studies in vitro and in vivo demonstrated their excellent capacity to target tumor cells and promote drug internalization, and significantly higher cytotoxicity with respect to that seen in a control group was shown for the nanoparticles. In addition, they have good thermal stability, photothermal conversion efficiencies (PCEs) and pH responsiveness, releasing more DOX in a mildly acidic environment, which is very conducive to their chemotherapeutic effectiveness in the tumor microenvironment. Fe3O4@PDA-PEG-cRGD-DOX NPs were used in a subcutaneous xenograft tumor model of nude mouse HCT-116 cells showed clear signal contrast in T2-weighted images and effective anti-tumor chemo-photothermal therapy under NIR irradiation.
Conclusion: According to our results, Fe3O4@PDA-PEG-cRGD-DOX had a satisfactory antitumor effect on colon cancer in nude mice and could be further developed as a potential integrated platform for the diagnosis and treatment of cancer to improve its antitumor activity against colon cancer.
Keywords: Fe3O4 nanoparticles, polydopamine, cRGD, magnetic resonance imaging, MRI, chemo-photothermal therapy, tumor target