111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

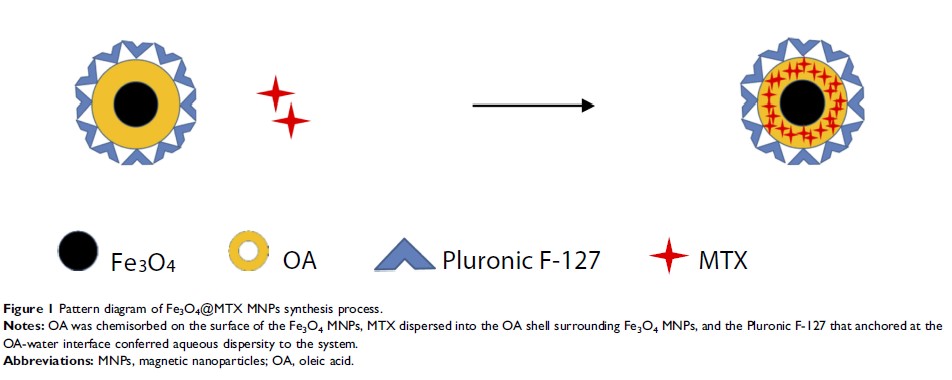
Fe3O4@MTX 磁性纳米粒子的制备和表征,用于原发性中枢神经系统淋巴瘤的体内外热化学疗法
Authors Dai X, Yao J, Zhong Y, Li Y, Lu Q, Zhang Y, Tian X, Guo Z, Bai T
Received 15 February 2019
Accepted for publication 13 November 2019
Published 5 December 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 9647—9663
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S205456
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: Primary central nervous system lymphomas (PCNSL) are extranodal malignant non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHL) that arise exclusively in central nervous system (CNS). Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common histological subtype.
Purpose: To evaluate whether nano drug-loading system-mediated magnetic-targeted thermochemotherapy could produce a better therapeutic effect than single chemotherapy while reducing the use of chemotherapeutic drugs.
Methods: Six groups (control, Fe3O4, MTX, Fe3O4@MTX, Fe3O4 with hyperthermia and Fe3O4@MTX with hyperthermia) were set. Tumor cell apoptosis in each treatment group was detected by flow cytometry. Apoptosis-related gene expressions Caspase-3, Bax and Bcl-2 were detected by qPCR and Western blot; intracranial tumor model of PCNSL was established by intracranial injection of OCI-LY18 tumor cells into BALB/c-Nude mice. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was used to monitor tumor progression and H&E staining was used to observe pathological changes of the tumor tissue.
Results: In vitro, compared with chemotherapy alone, apoptosis rate of Fe3O4@MTX mediated thermochemotherapy group was significantly increased, and expression of apoptosis-inducing gene Caspase-3 and Bax were significantly upregulated in OCI-LY18 cells, while expression of apoptosis-inhibiting Bcl-2 gene was significantly downregulated. In vivo, MRI showed successful generation of intracranial tumor, and tumor volume was significantly smaller in combined thermochemotherapy group than in single chemotherapy group. H&E staining result of tumor tissues in each group was consistent with MRI; tumor cells were significantly reduced in thermochemotherapy group. Expression of apoptosis-related gene Caspase-3 and Bax were significantly upregulated in tumor tissues, while expression of Bcl-2 gene was significantly downregulated.
Conclusion: These results demonstrated in vivo and in vitro that the combined thermochemotherapy of Fe3O4@MTX MNPs was superior to the single MTX chemotherapy with less dosage, which may promote apoptosis of DLBCL cells through the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway and provided a new way for the treatment of PCNSL.
Keywords: primary central nervous lymphoma, PCNSL, Fe3O4@MTX magnetic nanoparticles, MNPs, hyperthermia, OCI-LY18 cells