111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

TRIM44 通过 Akt/mTOR 信号通路促进大肠癌的增殖、迁移和侵袭
Authors Li C, Hu H, Yang X, Huang C, Yu X
Received 25 August 2019
Accepted for publication 14 November 2019
Published 9 December 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 10693—10701
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S228637
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
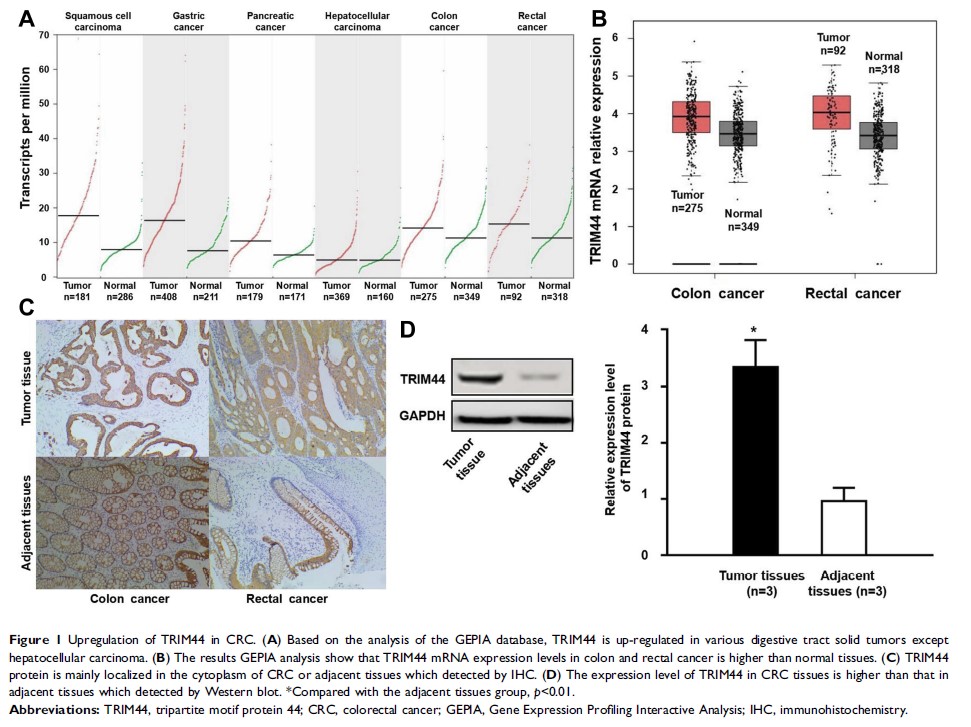
Purpose: The tripartite motif protein 44 (TRIM44) participates in a variety of biological processes of malignant tumors. However, the expression and molecular mechanism of TRIM44 in colorectal cancer (CRC) remain unclear.
Patients and methods: 123 CRC tissues were used for immunohistochemical assay and survival analysis. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) technology was used to silence the expression of TRIM44 in CRC cell lines. Then, we explored the effect of TRIM44 on the biological behavior of CRC cells. Finally, we studied the underlying mechanisms by Western blot.
Results: We found that TRIM44 is up-regulated in CRC tissues and cells. TRIM44 is a risk factor for poor prognosis in patients with CRC. In vitro, we effectively silenced the expression of TRIM44 in CRC cell lines. Silencing of TRIM44 inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of CRC cells. In terms of mechanistic studies, we found that high TRIM44 expression activates the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway.
Conclusion: Our research showed that TRIM44 may serve as a biomarker for CRC patients.
Keywords: TRIM44, CRC, prognosis, Akt/mTOR