111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

DNA 甲基转移酶抑制剂:抗肿瘤免疫反应的催化剂
Authors Dan H, Zhang S, Zhou Y, Guan Q
Received 30 May 2019
Accepted for publication 2 October 2019
Published 12 December 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 10903—10916
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S217767
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Jianmin Xu
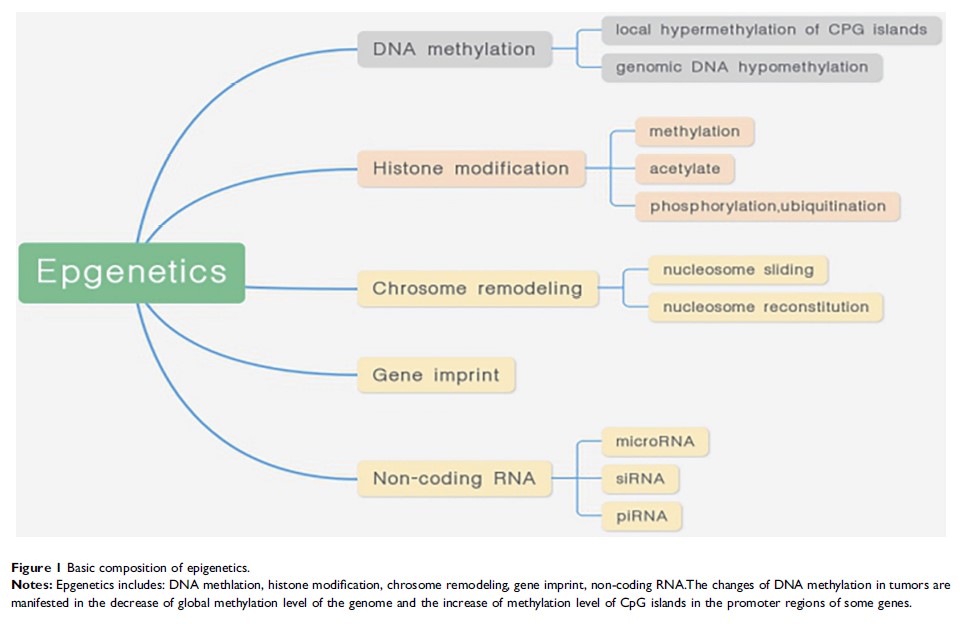
Abstract: Epigenetics is a kind of heritable change that involves the unaltered DNA sequence and can have effects on gene expression. The regulatory mechanism mainly includes DNA methylation, histone modification and non-coding RNA regulation. DNA methylation is currently the most studied aspect of epigenetics. It is widely present in eukaryotic cells and is the most important epigenetic mark in the regulation of gene expression in the cell. DNA methyltransferase inhibitors (DNMTi) have been increasingly recognized in the field of cancer immunotherapy, have been approved for the treatment of acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) and are widely being used in clinical trials of cancer immunotherapies. DNMTi promote the reactivation of tumour suppressor genes, enhance tumour immunogenicity, and stimulate a variety of immune cells to secrete cytokines that exert cytotoxic effects, promote tumour cell death, including macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells and CD8+ T cells, and upregulate major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I expression levels. Here, we mainly summarize the epigenetics related to DNMTi and their regulation of the antitumour immune response and DNMTi combined with immuno-therapeutics or histone deacetylase inhibitors to demonstrate the great development potential and clinical application value of DNMTi.
Keywords: DNA methyltransferase inhibitors, histone deacetylase inhibitor, immunomodulation, immune cells, immunotherapy, DNA methylation, epigenetics