111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

一线西妥昔单抗联合白细胞素、氟尿嘧啶和奥沙利铂(FOLFOX-4)与 FOLFOX-4 对 RAS 野生型转移性结直肠癌患者的成本效果分析比较
Authors Bai L, Zhang P, Zhou K, Liao W, Li Q
Received 13 June 2019
Accepted for publication 3 December 2019
Published 12 December 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 10419—10426
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S219318
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Beicheng Sun
Purpose: Compared with fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin (FOLFOX-4) alone, cetuximab plus FOLFOX-4 has shown superior performance in terms of efficacy and tolerability in patients with RAS wide-type (wt) metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) in the TAILOR trial (Trial No.: EMR62202-057; ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT01228734). Thus, we aimed to explore the cost-effectiveness of these two first-line regimens in patients with RAS wt mCRC from the Chinese societal perspective.
Methods: For the sake of executing the analysis, we used a Markov model containing three health states (progression-free survival (PFS), progressive disease (PD), and death) to simulate the process of RAS wt mCRC. The data regarding efficacy and safety were derived from the TAILOR trial. Transition probabilities were converted from the PFS and overall survival (OS) of both groups. Utility scores of the health states were obtained from previously published studies. Costs were computed from the perspective of Chinese society. The primary health outcome was the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER). Sensitivity analysis was utilized to investigate the effect of uncertainties on the Markov model.
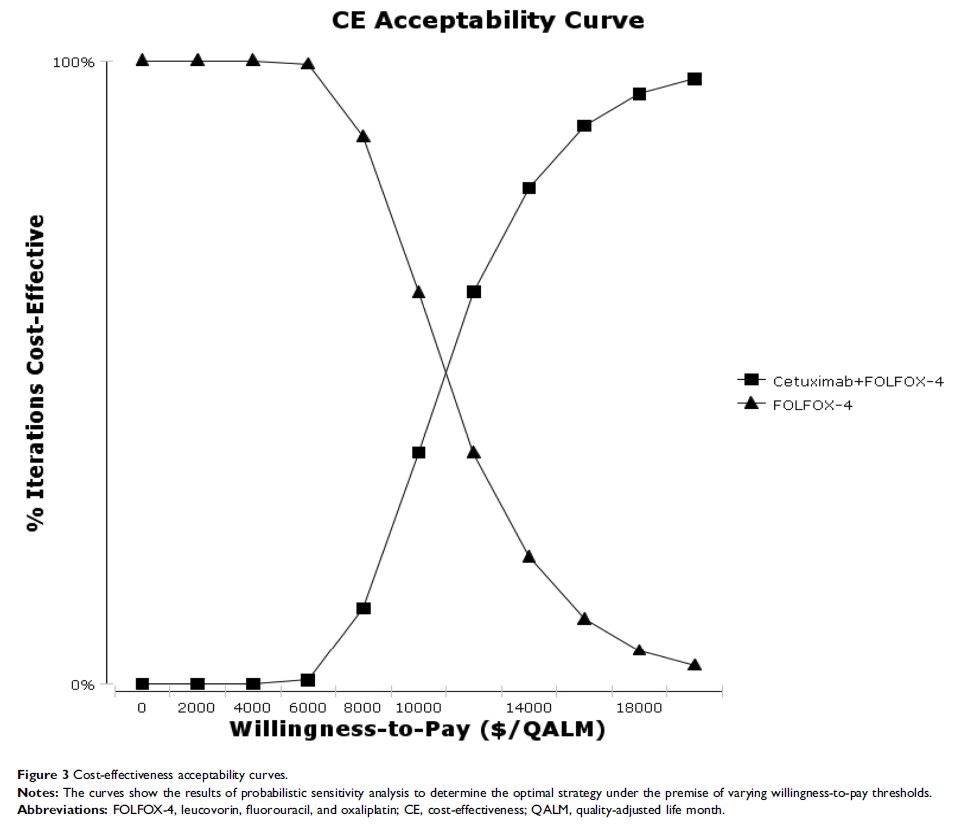
Results: Treatment with cetuximab plus FOLFOX-4 was estimated to provide an increase in quality adjusted-life years (QALYs) of 0.15 QALYs at an increased cost of $19,079 compared with FOLFOX-4 alone, resulting in an ICER of $127,193/QALY, which exceeded the threshold of willingness-to-pay (WTP) of $27,934/QALY in China. Sensitivity analysis showed that the cost of PFS in the cetuximab plus FOLFOX-4 arm was the most influential factor in the Markov model.
Conclusion: The combination of cetuximab and FOLFOX-4 is not a cost-effective strategy compared with FOLFOX-4 alone for the first-line treatment of patients with RAS wt mCRC from the perspective of Chinese society.
Keywords: cost-effectiveness, metastatic colorectal cancer, cetuximab, FOLFOX-4