111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

胺碘酮和奎尼丁的药物相互作用对依鲁司他(Eliglustat)在大鼠中的药代动力学影响
Authors Wang Q, Wang H, Zhong Y, Zhang Q
Received 12 August 2019
Accepted for publication 28 October 2019
Published 12 December 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 4207—4213
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S226948
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sukesh Voruganti
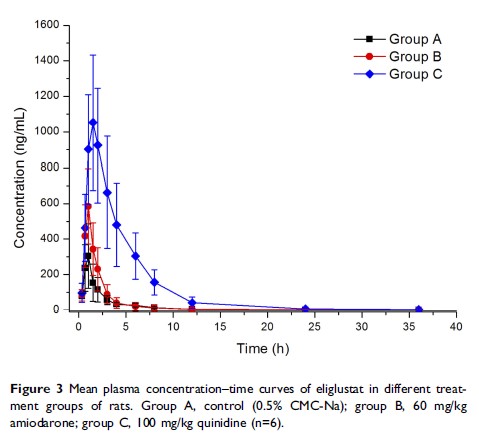
Background: Eliglustat, a new oral substrate-reduction therapy, was recently approved as a first-line therapy for Gaucher’s disease type 1 (GD1) patients.
Purpose: The purpose of the present study was to develop and validate a simple UPLC-MS/MS method for the measurement of plasma-eliglustat concentration and to investigate the effects of amiodarone and quinidine on eliglustat metabolism in rats.
Methods: Eighteen rats were randomly divided into three groups (n=6): control (0.5% CMC-Na, group A), amiodarone (60 mg/kg, group B), and quinidine (100 mg/kg, group C). Thirty minutes later, 10 mg/kg eliglustat was orally administered to each rat and concentrations of eliglustat in the rats determined by our UPLC-MS/MS method.
Results: Amiodarone and quinidine increased the main pharmacokinetic parameters (AUC0→t , AUC0→∞, and Cmax) of eliglustat significantly and decreased clearance obviously.
Conclusion: Amiodarone and quinidine can elevate eliglustat exposure and have an inhibitory effect on eliglustat metabolism. Clearly, appropriate pharmacological studies of eliglustat in patients treated with amiodarone or quinidine should be done in future.
Keywords: eliglustat, drug–drug interaction, UPLC-MS/MS, amiodarone, quinidine