111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA BCAR4 通过靶向 miR-2276 来上调胶质瘤中 MMP7 的表达,从而促进生长、侵袭和致瘤性
Authors Wang Z, Wang L, Liang Z, Xi Y
Received 5 August 2019
Accepted for publication 13 November 2019
Published 12 December 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 10963—10973
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S226026
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Objective: Long non-coding RNA breast cancer anti-estrogen resistance 4 (BCAR4) has been recognized as a proto-oncogene in various malignancies. It has been reported to be highly expressed and promote cell proliferation in glioma. However, its additional roles in gliomagenesis remain largely unclear. This research intends to investigate the impact and internal molecular mechanism of BCAR4 on glioma cell growth, invasion and tumorigenesis.
Methods: BCAR4 expression was examined by qPCR in 30 cases of graded glioma specimens and 7 glioblastoma (GBM) cell lines compared with respective controls. Its potential prognostic value was evaluated by Kaplan–Meier survival analysis. The biological roles of BCAR4 in gliomagenesis were verified by CCK-8, transwell and intracranial xenograft assays successively. qPCR and RNA pull-down assays were applied to study the relationship between BCAR4 and miR-2276. Then, qPCR, Western blot and luciferase reporter assays were used to validate the targeting of matrix metallopeptidase 7 (MMP7) by miR-2276 and the regulation of MMP7 by BCAR4. Finally, MMP7 was restored in BCAR4-silenced GBM cells and the rescue effects were determined by CCK-8 and transwell assays.
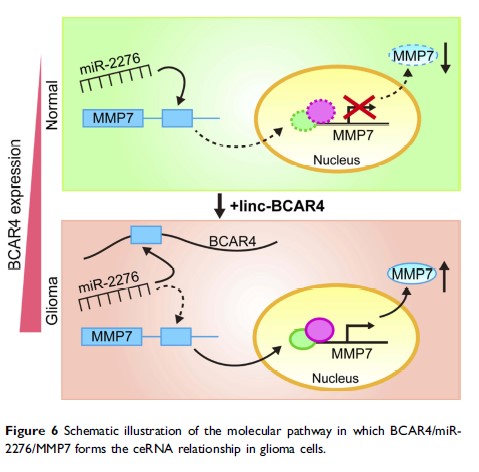
Results: BCAR4 expression was increased in glioma tissues and GBM cell lines, and its high expression positively correlated with advanced grades and worse prognosis. Functional assays verified that knockdown of BCAR4-inhibited cell growth and invasion in vitro, and impaired tumor formation in vivo. Mechanistically, we found that BCAR4 could act as a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) by targeting miR-2276 to upregulate MMP7 expression. Importantly, MMP7 restoration effectively rescued the inhibitory modulations on GBM cell growth and invasion caused by BCAR4 knockdown.
Conclusion: Our findings identified the essential roles of the BCAR4/miR-2276/MMP7 axis in gliomagenesis and provided novel insights on glioma therapy.
Keywords: glioma, BCAR4, ceRNA, miR-2276, MMP7