111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Beclin 1 的杂合破坏可减轻氧化锌纳米颗粒引起的对小鼠肝脏胆固醇生物合成的干扰
Authors Liu X, Wang B, Jiang X, Zhang J, Tang Q, Zhang Y, Qin X, Chen C, Zou Z
Received 22 July 2019
Accepted for publication 21 November 2019
Published 12 December 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 9865—9875
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S224179
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Purpose: Liver is regarded as one of the primary target organs for zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs) toxicity. Since liver represents the leading site for de novo cholesterol biosynthesis in mammals, the injuries of liver could result in the disruption of cholesterol biosynthesis. In this study, we aimed to investigate whether pulmonary ZnONPs exposure induces disturbance of cholesterol biosynthesis in mouse liver.
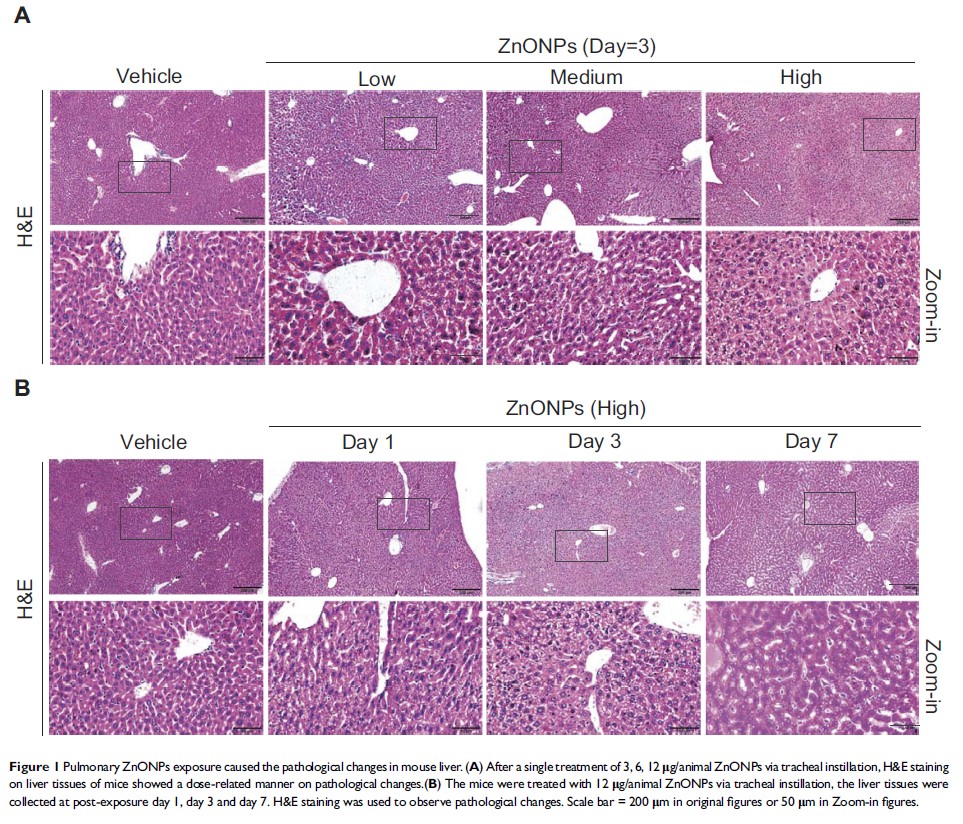
Methods and results: Our data demonstrated intratracheally instilled with a single dose of 3, 6, and 12 μg/animal ZnONPs could induce histopathological deterioration in mouse liver in a dose-related manner at 3 days, but remission was observed at 7 days after treatment. Moreover, ZnONPs caused the disturbance of cholesterol biosynthesis by increasing both 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA) reductase and sterol regulatory element-binding protein 2 (SREBP2) protein expressions. To further reveal the underlying toxic mechanisms, we detected the biomarkers of autophagy and found that pulmonary ZnONPs exposure led to the elevation of LC3B-II and Beclin 1, suggesting ZnONPs might trigger autophagy in liver tissues. By using both beclin 1 +/+ and beclin 1 +/- mice, we demonstrated that inhibition of autophagy by heterozygous disruption of beclin 1 attenuated the disturbance of cholesterol biosynthesis induced by ZnONPs in liver.
Conclusion: Pulmonary exposure of ZnONPs would induce the cholesterol biosynthesis disturbance in mouse liver through Beclin-1-dependent autophagy activation, suggesting that inhibition of autophagy may contribute to preventing the cholesterol biosynthesis disturbance and its associated pathologies induced by ZnONPs in liver.
Keywords: zinc oxide nanoparticles, cholesterol biosynthesis, autophagy, beclin 1 , liver