111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

交互式网络平台提高了过敏性鼻炎患者皮下免疫治疗的依从性和疗效
Authors Shen Z, Tan G, Zhong Z, Ding S, Wang F
Received 23 October 2019
Accepted for publication 9 December 2019
Published 13 December 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 2101—2110
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S235711
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Naifeng Liu
Background: Allergic rhinitis (AR) is a common chronic inflammatory disease of nasal mucosa worldwide, and its symptoms seriously affect the lives of patients. Subcutaneous immunotherapy (SCIT) is an effective treatment for AR, but it is also associated with low patient compliance and difficulties in fully achieving therapeutic effects.
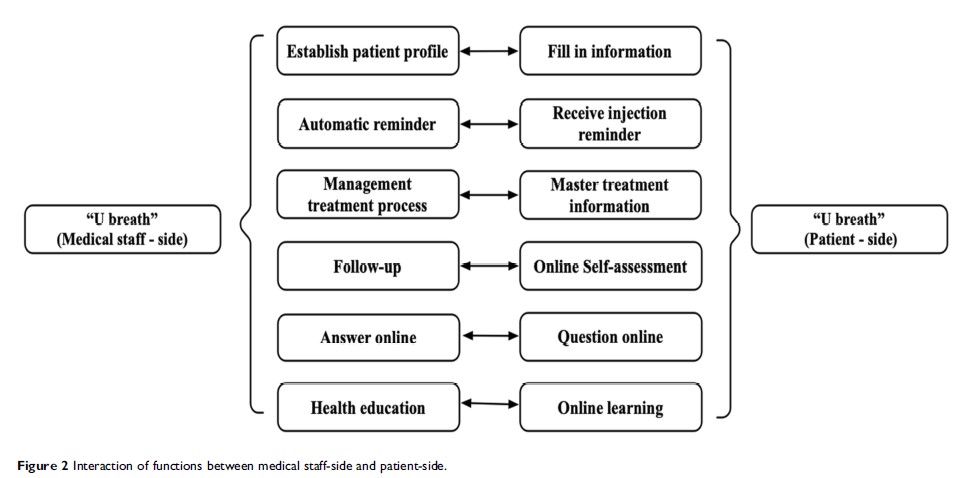
Objective: In this prospective randomized controlled study, we verified the effects of an interactive network platform named “U breath” in improving patient compliance and the efficacy of SCIT in patients with AR.
Methods: A total of 148 patients who received SCIT were recruited as participants and randomly assigned to either the standardized management (SM) or the interactive network platform management (INP) group. The SM group experienced the standard management SCIT process. The INP group experienced a new management approach based on an interactive network platform called “U breath”. The compliance rate, combined symptom and medication score (CSMS), visual analogue scale score and the rhinoconjunctivitis quality of life questionnaire (RQLQ) results were evaluated at baseline and 1-year postintervention for the two groups.
Results: Within the first year of treatment, the INP group had a higher compliance rate than did the SM group, with a statistically significant difference (P<0.05). The INP group showed better clinical improvement than the SM group did in terms of the VAS score, and the RQLQ score except the sleep problems (P< 0.05).
Conclusion: This study confirmed that the application of an interactive network platform is of great significance for improving patient compliance and the treatment effects of SCIT in patients with AR.
Keywords: allergic rhinitis, subcutaneous immunotherapy, compliance, quality of life, network, management