111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

MicroRNA-937-3p 在乳腺癌患者中的致癌作用和预后价值
Authors Li D, Zhong J, Zhang G, Lin L, Liu Z
Received 2 September 2019
Accepted for publication 16 November 2019
Published 13 December 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 11045—11056
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S229510
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Arseniy Yuzhalin
Purpose: Breast cancer is the most common female tumor in the world. MicroRNA has been reported to play an important role in the progression of breast cancer. The purpose of this study was to explore the role of miR-937-3p in breast cancer.
Patients and methods: Expression of miR-937-3p in breast cancer tissues and serums was detected from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and patients’ samples. Kaplan–Meier plotter identified the association between miR-937-3p and prognosis.
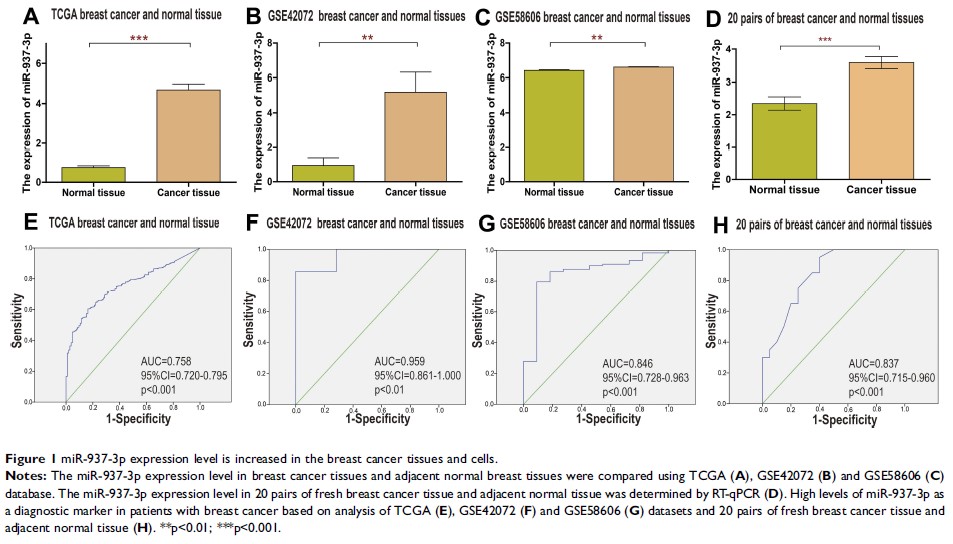
Results: The analysis of TCGA, GEO and qRT-PCR suggested that the level of miR-937-3p was increased in breast cancer tissues and serum compared with adjacent normal breast tissues and healthy persons, respectively. The decreased expression of miR-937-3p inhibited breast cancer proliferation, migration and invasion. CCRL2 was the target of miR-937-3p. In contrast to miR-937-3p, the level of CCRL2 was decreased in breast cancer tissues. Luciferase reporter assay revealed that miR-937-3p directly bound to the 3ʹ-UTR of CCRL2. Double knockdown of CCRL2 and miR-937-3p promoted breast cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion, suggesting that miR-937-3p promoted breast cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting CCRL2. The Kaplan–Meier survival analysis suggested that breast cancer patients with high level of miR-937-3p or low level of CCRL2 had a reduced overall survival (OS).
Conclusion: miR-937-3p plays an important role in the diagnosis and prognosis of breast cancer. Inhibition of miR-937-3p expression may be a novel targeted therapy for breast cancer.
Keywords: miR-937-3p, breast cancer, proliferation, migration, invasion, prognosis