111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

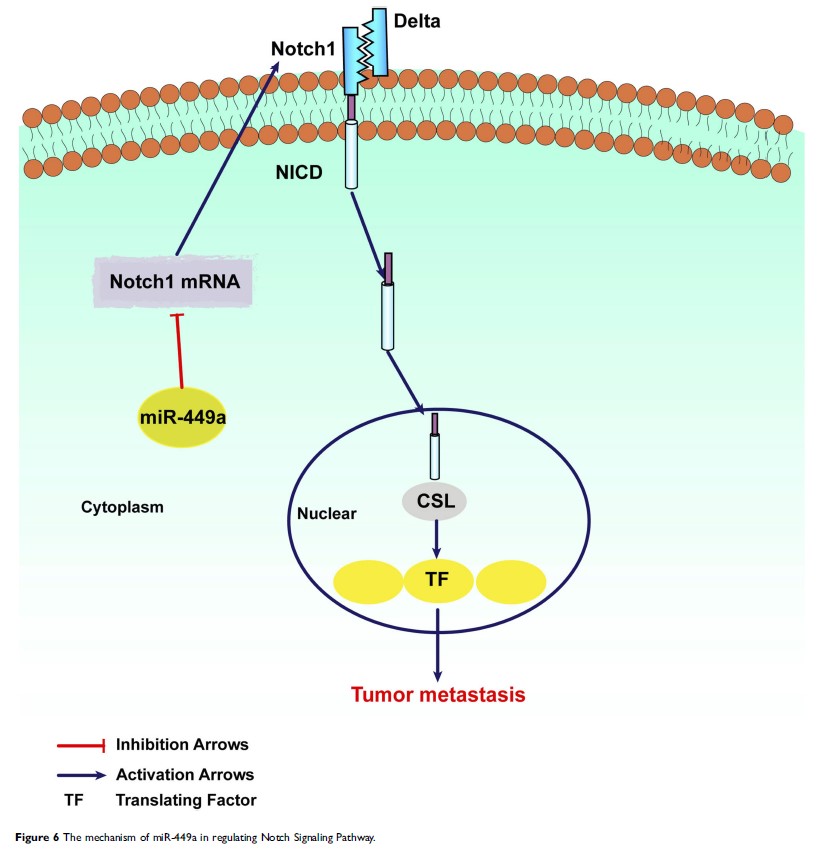
miR-449a 与肝细胞癌的短期复发有关,并通过靶向 Notch1 来抑制迁移和侵袭
Authors Han B, Huang J, Yang Z, Zhang J, Wang X, Xu N, Meng H, Wu J, Huang Q, Yang X, Shen R, Sun C
Received 24 May 2019
Accepted for publication 19 November 2019
Published 13 December 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 10975—10987
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S216997
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Nicola Silvestris
Purpose: To explore the effect of miR-449a inhibits migration and invasion by targeting Notch1 and regulating epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and further study on the molecular mechanism.
Patients and methods: The expression of miR-449a and Notch1 in HCC cells and tissues was detected by qRT-PCR. The HCC cell line HCCLM3 and SMMC-7721 were transfected with miR-449a. The invasion and migration of HCC cell lines were detected by transwell assay and wound healing assay. The Notch pathway and EMT related protein were detected with Western Blotting. The specific binding site of mir-449a on notch1 gene was detected by luciferase assay.
Results: We found the expression of miR-449a was related to short-term recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy and acted as independent risk factors of DFS and OS. The expression of miR-449a decreased in tumor tissues and HCC cell lines, but the expression of Notch1 increased. The overexpressed miR-449a promoted the invasiveness in vitro by regulating EMT via Notch pathway. Mechanically, miR-449a inhibited the translation of Notch1 protein by binding to 3ʹ UTR of its mRNA directly.
Conclusion: miR-449a is short-term recurrence-related miRNA and inhibits the invasion and metastasis ability of HCC cells by regulating EMT via Notch pathway. miR-449a may be a new effective therapeutic target for HCC.
Keywords: signal pathway, microRNA, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, bioinformatics