111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

CDK4/6 抑制剂帕博西尼通过介导细胞凋亡及抑制 DNA 损伤修复来增强鼻咽癌细胞的放射敏感性
Authors Xie X, Zheng W, Chen T, Lin W, Liao Z, Liu J, Ding Y
Received 10 October 2019
Accepted for publication 26 November 2019
Published 16 December 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 11107—11117
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S234221
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Gaetano Romano
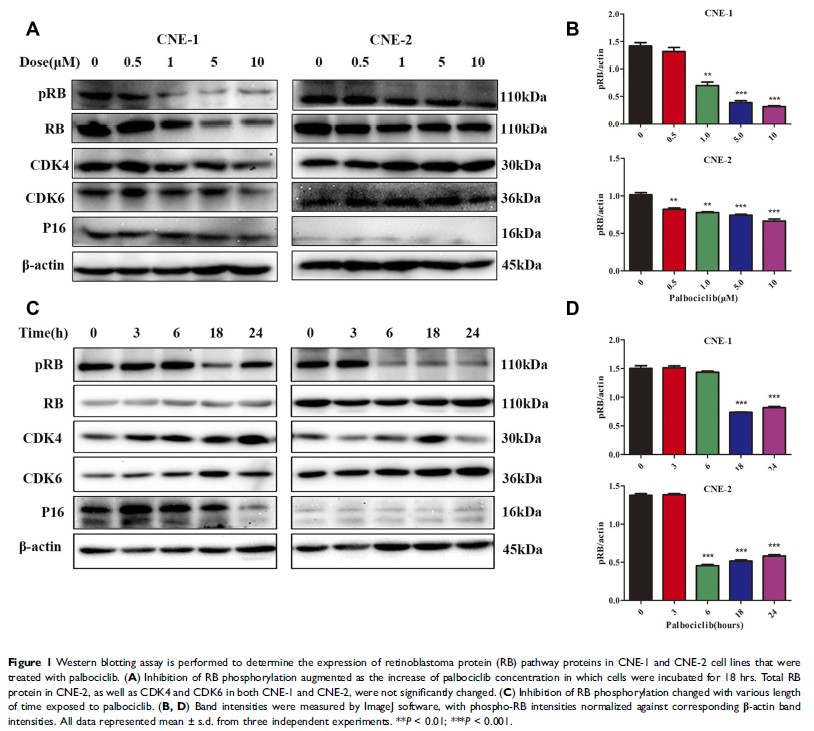
Background: Radiotherapy is the primary approach for nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). Although high survival rates can be obtained with radiation for early stage lesions, distant metastasis and local recurrence frequently occur. In this study, we pioneeringly investigated the antitumor activity and underlying mechanism of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor (palbociclib) combined with radiation on NPC cells.
Methods: Evaluation of radiation enhancement with palbociclib was based on results from CCK8 and clonogenicity assays for cell proliferation, flow cytometry for apoptosis, ROS level and cell cycle and immunocytochemistry for DNA double-strand break repair.
Results: Palbociclib inhibited cellular growth of RB-proficient CNE-1 and CNE-2 via reducing RB phosphorylation and arresting cell cycle. Combination regimens of palbociclib plus radiation were significantly superior to palbociclib or radiation only through inhibiting cellular growth and inducing apoptosis. Moreover, the antitumor activity of both concurrent palbociclib plus radiation and radiation followed by palbociclib consistently preceded that of palbociclib followed by radiation. Meanwhile, the two preferable combination regimens possessed higher proportion of G2/M phase cells, evidently inhibited DNA double-strand break repair and eventually triggered tumor cell apoptosis.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrated that palbociclib could provoke a strong antitumor activity as a potential adjuvant to radiation therapy for NPC harboring RB expression.
Keywords: nasopharyngeal carcinoma, palbociclib, radiotherapy, apoptosis, DNA damage repair