111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-7 通过靶向 MRP1 和 BCL2 逆转乳腺癌对化疗的耐药性
Authors Hong T, Ding J, Li W
Received 28 April 2019
Accepted for publication 7 October 2019
Published 16 December 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 11097—11105
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S213780
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Arseniy Yuzhalin
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of non‐coding RNAs that have been linked with breast cancer chemoresistance, which is a major clinical problem causing disease relapse and poor prognosis. miR-7 exerts several tumor suppressive activities.
Purpose: This study was designed to clarify whether and how miR-7 regulates breast cancer chemoresistance.
Methods: miR-7 level in breast cancer was determined by qRT-PCR analysis. Cell viability was assessed by MTS assay to quantify the IC50 value of paclitaxel and carboplatin. The targets of miR-7 were confirmed by luciferase reporter assay.
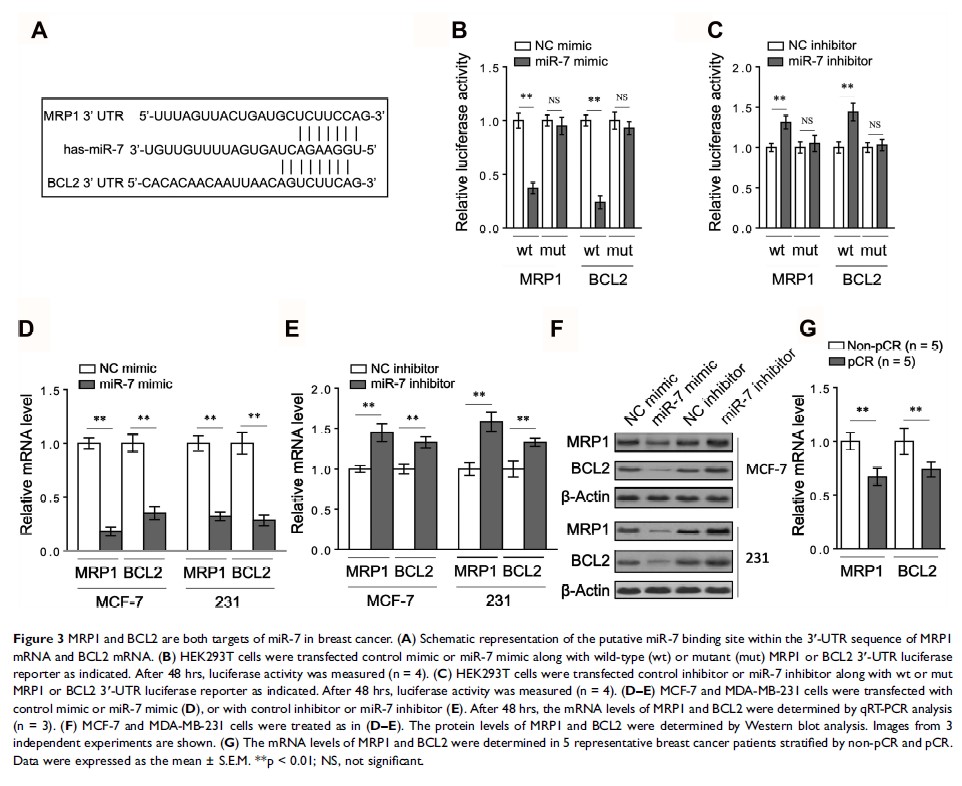
Results: Higher miR-7 expression predicts better pathological complete response (pCR) of breast cancer patients receiving paclitaxel/carboplatin chemotherapy. In vitro, miR-7 sensitizes breast cancer cell lines (MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231) to paclitaxel and carboplatin, alone and in combination. In addition, we reveal that both the multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 (MRP1) and anti-apoptotic B cell lymphoma 2 (BCL2) are targets of miR-7 in breast cancer cells. Furthermore, miR-7-induced sensitization of breast cancer to paclitaxel/carboplatin is markedly reversed by restoration of MRP1 and BCL2.
Conclusion: These findings show that miR-7 reverses breast cancer chemoresistance through suppressing MRP1 and BCL2, and also suggest that miR-7 may possess a predictive value and represent a therapeutic target in breast cancer chemotherapy.
Keywords: miR-7, breast cancer, pathological complete response, chemoresistance, MRP1, BCL2