111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

中国老年人轻度认知障碍与健康相关的生活质量之间的关联
Authors Song D, Yu DSF, Li PWC, He G, Sun Q
Received 19 August 2019
Accepted for publication 1 December 2019
Published 16 December 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 2205—2212
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S227767
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Zhi-Ying Wu
Purpose: This study aimed to assess the health-related quality of life (HRQoL) and identify the important correlates of HRQoL in older Chinese adults with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).
Patients and methods: A cross-sectional study design was adopted. A total of 204 older adults with MCI were enrolled in this study. HRQoL was evaluated by the Quality of Life–Alzheimer’s disease. Hierarchical regression analysis was conducted to investigate the sociodemographic, disease-related, psychological, and behavioral factors associated with the HRQoL of individuals with MCI.
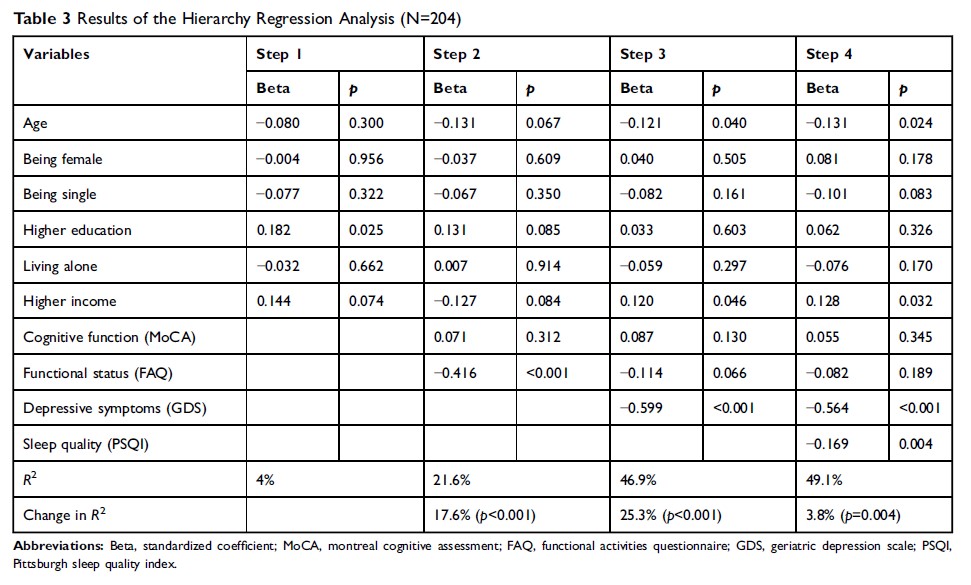
Results: Hierarchical regression analysis indicated that old age (Beta = −0.131, p =0.024), low income (Beta = 0.128, p = 0.032), depressive symptoms (Beta = −0.564, p < 0.001), and poor sleep quality (Beta = −0.169, p =0.004) were significantly associated with the HRQoL of individuals with MCI.
Conclusion: Caring for older Chinese adults with MCI should focus on sociodemographically disadvantaged groups with advanced age and low income. Rehabilitation programs that effectively alleviate depressive symptoms and improve sleep quality should be applied to older adults with MCI to enhance their HRQoL.
Keywords: mild cognitive impairment, health-related quality of life, correlates