111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

lncRNA TDRG1 敲除可通过 PI3K/AKT/mTOR 信号通路抑制子宫内膜癌的肿瘤发生
Authors Sun R, Sun X, Liu H, Li P
Received 21 August 2019
Accepted for publication 21 November 2019
Published 11 December 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 10863—10872
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S228168
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
Background and objective: Endometrial carcinoma (EC) is one of the most frequently diagnosed malignancies in females. Dysregulation of lncRNA TDRG1 has been widely documented in several cancers, including EC. However, the mechanism of this lncRNA involving in EC progression remains to be further elucidated.
Materials and methods: The enrichment levels of TDRG1 in EC tissues and cell lines were examined by RT-qPCR. Flow cytometry, cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8), transwell, and Western blot assays were conducted to assess whether TDRG1 knockdown could affect cell cycle arrest, proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of EC cells. The phosphorylation levels of mTOR, AKT and PI3K that associated with PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway were determined by Western blot assay.
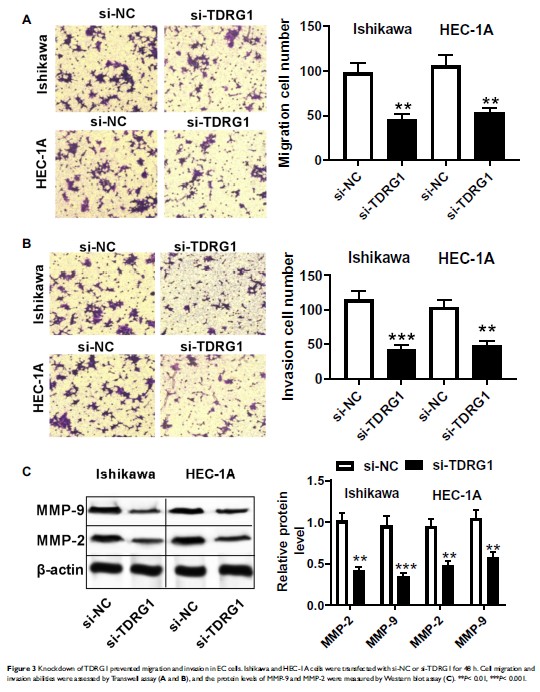
Results: TDRG1 expression was markedly upregulated in EC tissues and cell lines. Knockdown of TDRG1 significantly induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis, inhibited cell proliferation, restrained the invasion and migration abilities in EC cells. Moreover, TDRG1 silencing decreased the protein levels of p-AKT, p-PI3K, and p-mTOR of EC cells.
Conclusion: Our data underlined the implication of TDRG1 in EC progression, proposing that targeting TDRG1 might be a potential therapeutic avenue in EC.
Keywords: endometrial carcinoma, TDRG1, PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway