111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

金茶花提取物通过诱导自噬和细胞凋亡增强胃癌细胞对紫杉醇的敏感性
Authors He X, Li H, Zhan M, Li H, Jia A, Lin S, Sun L, Du H, Yuan S, Li Y
Received 22 June 2019
Accepted for publication 9 November 2019
Published 11 December 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 10811—10825
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S220453
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr XuYu Yang
Background: Camellia nitidissima Chi (CNC) has been applied as a traditional folk medicine for the effective treatment of various diseases. However, there is little research regarding the mechanism of CNC on pharmaceutical function including anticancer effect.
Materials and methods: JHC-4 is a n-butanol extract from CNC. The anti-proliferation effect was evaluated by MTT assays. Monodansylcadaverine (MDC) staining, Western blotting and autophagy inhibitors (CQ and BafA1) were applied to determine whether JHC-4 induced autophagy. The synergistic anticancer effect was evaluated by MTT assays, flow cytometry, Western blotting and autophagy inhibitors. Western blotting was used to explore the influence of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway induced by drug treatment.
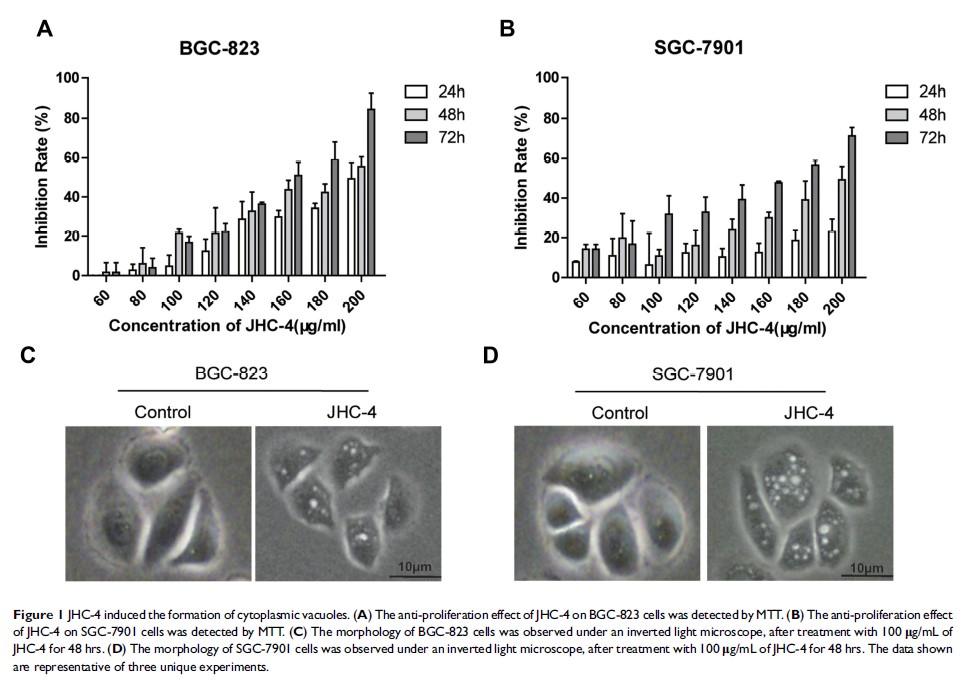
Results: JHC-4 caused significant growth inhibition and induced autophagy in human gastric cancer cells. Moreover, JHC-4 as an autophagy agonist synergistically potentiated the sensitivity of gastric cancer cells to paclitaxel. Meanwhile, JHC-4 could significantly enhance the growth inhibition effect of paclitaxel by the induction of autophagy and apoptosis. Finally, we demonstrated that the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway was involved in the synergistic anti-proliferation effect of JHC-4 and paclitaxel.
Conclusion: All these data indicated that JHC-4 was a novel autophagy inducer when combination with paclitaxel for gastric cancer, which provided the scientific evidence for the use of this Chinese traditional medicine against cancer.
Keywords: Camellia nitidissima Chi , paclitaxel, autophagy, apoptosis, PI3K/Akt/mTOR