110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

甲状腺切除术后甲状腺癌患者生活质量评分降低的危险因素
Authors Li J, Xue LB, Gong XY, Yang YF, Zhang BY, Jin J, Shi QF, Liu YH
Received 19 October 2019
Accepted for publication 4 December 2019
Published 19 December 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 10593—10598
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S235323
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Objective: Despite the expectation of normal life expectancy for thyroid cancer, there are concerns about the decreased quality of life (QoL). The present study investigated the potential risk factors of deterioration in QoL scores in thyroid cancer patients after thyroidectomy.
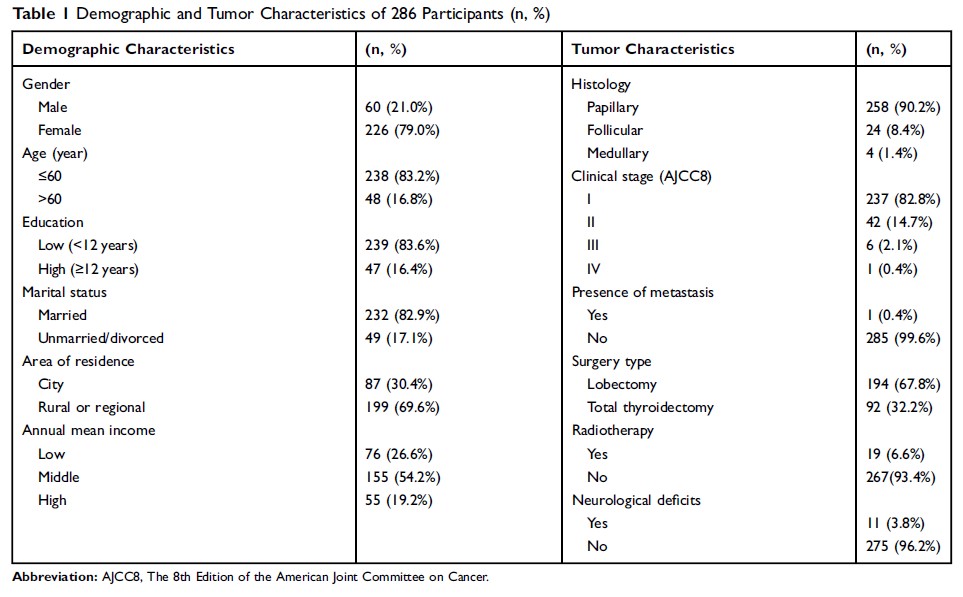
Materials and methods: A total of 286 patients who were diagnosed with thyroid cancer after thyroidectomy were involved in this prospective, single-center, observational study from November 2018 to June 2019. The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire Core 30 was used to assess the QoL 3 months after thyroidectomy. We investigated the effects of demographics (age, gender, education, marital status, area of residence, and annual mean income), tumor characteristics (histology, clinical stage, presence of metastasis, surgery type, and radiotherapy), and neurological deficits induced by recurrent nerve or superior laryngeal injury on QoL.
Results: The mean overall QoL in thyroid cancer survivors was 65.93 ±9.00 (on a scale of 0–100, where 100 was the best). Multivariate regression analysis confirmed that clinical stage (P < 0.010), surgery type (P < 0.001), histology (P < 0.001), neurological deficits (P < 0.001), and marital status (P < 0.001) were independent risk factors for decreased QoL 3 months after thyroidectomy.
Conclusion: Our study indicated that clinical stage, surgery type, histology, neurological deficits, and marital status were independent risk factors for decreased QoL at 3 months after thyroidectomy. Further exploration and validation of these findings in larger prospective studies are warranted.
Keywords: quality of life, thyroid cancer, thyroidectomy