110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

应用生长抑素、化疗联合 TAE 治疗伴有坏死松解性游走性红斑的异质性胰高血糖素瘤
Authors Shen C, He J, Le X, Zheng L, Cao D
Received 7 November 2019
Accepted for publication 7 December 2019
Published 20 December 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 11339—11344
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S237634
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Takuya Aoki
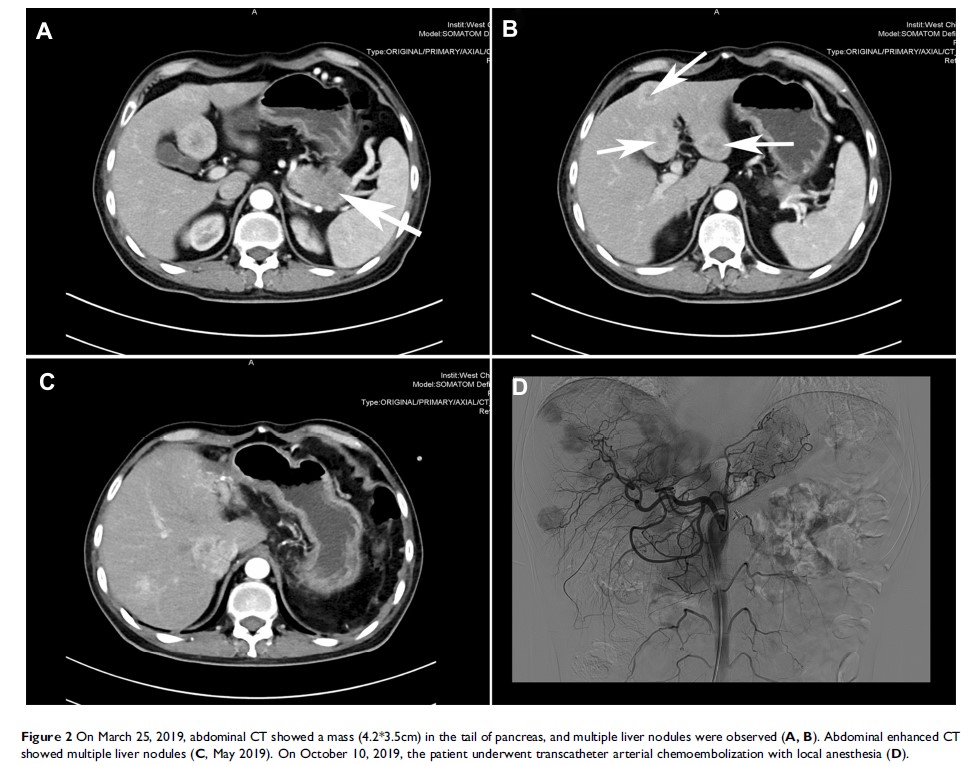
Abstract: Glucagonoma, a rare neuroendocrine tumor of the pancreas, which is often misdiagnosed because of non-characteristic clinical manifestations. In addition, the treatment has not been well established for this disease so far. We here report a case of glucagonoma previous misdiagnosed as recurrent erythema. In this case, necrolytic migratory erythema was the main clinical manifestation, and he received surgical resection after admission although with liver metastasis. Postoperative pathological results showed that the heterogeneity of proliferative index in primary (Ki-67: 5∼10%) and metastatic (Ki-67: 25∼30%) tumors were obviously observed. One month postoperatively, abdominal CT and MRI showed multiple liver metastasis (type III) again. Interestingly, the skin rash was obviously improved after treatment with somatostatin combined with chemotherapy (octreotide, temozolomide and capecitabine). Subsequently, the patient received transarterial embolization (TAE). Up to now, no progression was noted for liver metastasis. Due to its rarity, clinical diagnosis is challenging; thus, further understanding of the disease by clinicians is helpful for early diagnosis and treatment, so as to improve the prognosis of patients.
Keywords: glucagonoma, necrolytic migratory erythema, somatostatin, chemotherapy, TAE