110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
Fe3O4 与藤黄酸 (gambogic acid) 结合的磁性纳米粒子对 SMMC-7721 细胞系凋亡的影响
Authors Tian L, Chen BA, Cheng J, Guo QL
Received 12 April 2015
Accepted for publication 16 July 2015
Published 26 August 2015 Volume 2015:8 Pages 2285—2290
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S86494
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 5
Editor who approved publication: Dr Faris Farassati
Objective: This study aims to investigate the potential benefit of combination therapy with magnetic nanoparticles of Fe3O4 (Fe3O4-MNP) and gambogic acid (GA) on SMMC-7721 cells.
Methods: The inhibition of proliferation of SMMC-7721 cells was evaluated by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium
bromide assay. Cell apoptosis was calculated and analyzed by flow cytometry, and the expressions of the apoptosis-related protein were detected by Western blot.
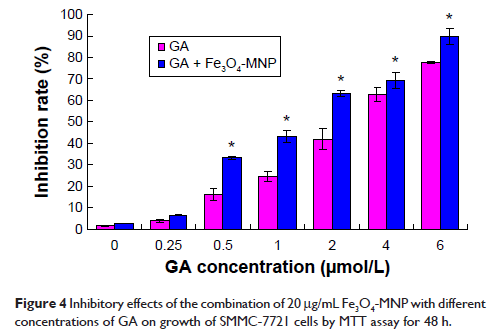
Results: GA enhanced the cytotoxicity of SMMC-7721 cells in a dose-dependent manner. The Fe3O4-MNP itself had no obviously inhibitory effect, but it could enhance the effect of GA on proliferation of SMMC-7721 cells. The apoptotic rate of SMMC-7721 cells induced by combination of GA with Fe3O4-MNP was higher than that by GA alone. The expression levels of caspase-3 and caspase-8 after co-treatment of GA and Fe3O4-MNP were higher than that exposed to either GA or Fe3O4-MNP alone, while the levels of bcl-2 were downregulated.
Conclusion: Fe3O4-MNP can promote GA-induced apoptosis of SMMC-7721 cells, which may be related to the downregulation of Bcl-2 and upregulation of caspase-3.
Keywords: primary hepatocellular carcinoma, traditional Chinese medicine, anti-tumor activity, targeted-drug carrier
Methods: The inhibition of proliferation of SMMC-7721 cells was evaluated by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium
bromide assay. Cell apoptosis was calculated and analyzed by flow cytometry, and the expressions of the apoptosis-related protein were detected by Western blot.
Results: GA enhanced the cytotoxicity of SMMC-7721 cells in a dose-dependent manner. The Fe3O4-MNP itself had no obviously inhibitory effect, but it could enhance the effect of GA on proliferation of SMMC-7721 cells. The apoptotic rate of SMMC-7721 cells induced by combination of GA with Fe3O4-MNP was higher than that by GA alone. The expression levels of caspase-3 and caspase-8 after co-treatment of GA and Fe3O4-MNP were higher than that exposed to either GA or Fe3O4-MNP alone, while the levels of bcl-2 were downregulated.
Conclusion: Fe3O4-MNP can promote GA-induced apoptosis of SMMC-7721 cells, which may be related to the downregulation of Bcl-2 and upregulation of caspase-3.
Keywords: primary hepatocellular carcinoma, traditional Chinese medicine, anti-tumor activity, targeted-drug carrier