110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

基于 microRNA 的胃癌治疗研究进展
Authors Zhao X, Hu GF, Shi YF, Xu W
Received 30 June 2019
Accepted for publication 10 December 2019
Published 24 December 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 11393—11411
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S221354
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr XuYu Yang
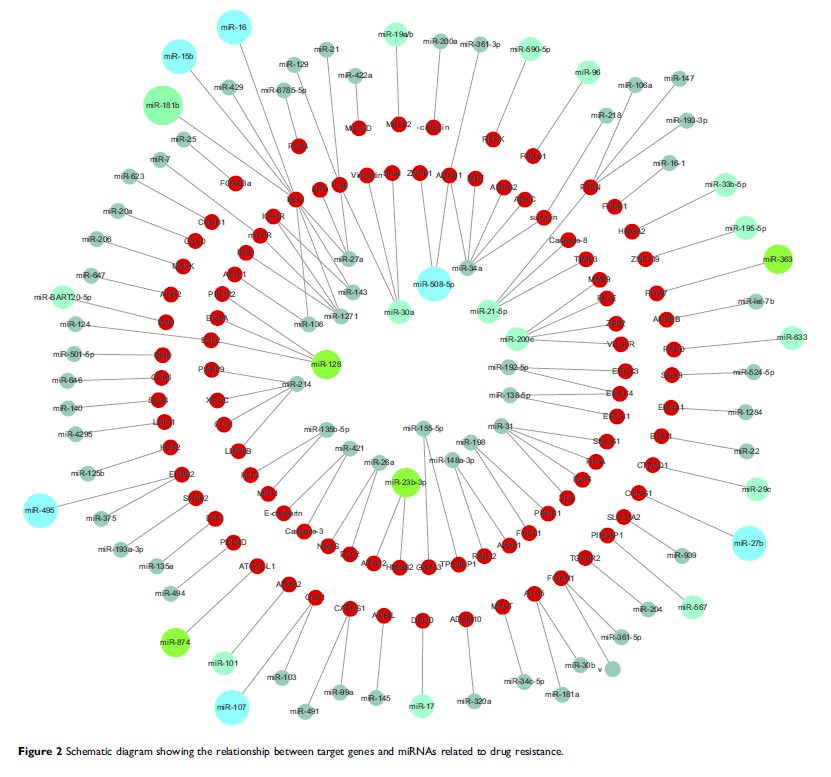
Abstract: Gastric cancer (GC) is one of the leading causes of tumor-related mortality. In addition to surgery and endoscopic resection, systemic therapy remains the main treatment option for GC, especially for advanced-stage disease and for cases not suitable for surgical therapy. Hence, improving the efficacy of systemic therapy is still an urgent problem to overcome. In the past decade, the essential roles of microRNAs (miRNAs) in tumor treatment have been increasingly recognized. In particular, miRNAs were recently shown to reverse the resistance to chemotherapy drugs such as 5-fluorouracil, cisplatin, and doxorubicin. Synthesized nanoparticles loaded with mimics or inhibitors of miRNAs can directly target tumor cells to suppress their growth. Moreover, exosomes may serve as promising safe carriers for mimics or inhibitors of miRNAs to treat GC. Some miRNAs have also been shown to play roles in the mechanism of action of other anti-tumor drugs. Therefore, in this review, we highlight the research progress on microRNA-based therapy in GC and discuss the challenges and prospects associated with this strategy. We believe that microRNA-based therapy has the potential to offer a clinical benefit to GC patients, and this review would contribute to and motivate further research to promote this field toward this ultimate goal.
Keywords: therapeutics, drug resistance, nanoparticles, treatment mechanism