110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

吴茱萸碱通过触发内源性凋亡信号通路的激活来选择性地抑制多发性骨髓瘤细胞的生长
Received 23 October 2019
Accepted for publication 6 December 2019
Published 24 December 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 11383—11391
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S235730
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjay Singh
Introduction: Evodiamine (Evo) is one of the main bioactive components derived from the drying mature fruit of the genus Evodia rutaecarpa (Juss.) Benth. Although Evo has shown its anti-cancer activity in several cancers, the effects on multiple myeloma (MM) remain unknown. In this study, we aim to investigate the cytotoxic role of Evo on MM cells.
Methods: CCK-8 assay, apoptotic cell analysis, xenografted mice model, caspase activity assay and mitochondrial membrane potential assay were performed.
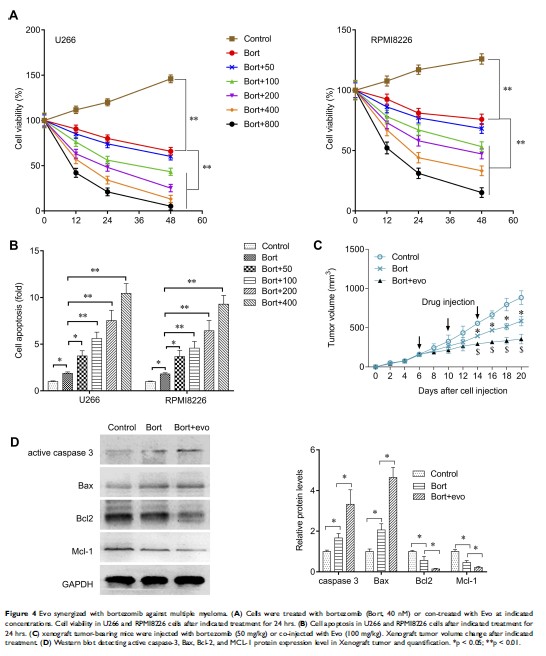
Results: We found that Evo selectively inhibits cell proliferation and increases apoptosis rate in MM cells, but not in healthy B lymphocytes, in a time and dose-dependent manner. Evo treatment significantly activated caspase-3 and −9 in MM cells. Evo also increased cytochrome C expression and ROS production in cytosol in a dose-dependent manner, which was abolished by MitoTEMPO cotreatment. In addition, co-treatment with bortezomib and Evo showed a more potent reduction of cell viability and a higher apoptosis than that of bortezomib single treatment in U266 and RPMI8226 cells.
Conclusion: We provided evidence to demonstrate that Evo selectively suppresses cell growth and increases apoptosis rate in MM cells through the intrinsic apoptosis pathway. Application of Evo and bortezomib might enhance the anti-cancer effect on MM cells.
Keywords: evodiamine, mitochondria, intrinsic apoptosis, bortezomib, resistance