110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

抑制类端粒沉默干扰体 1 可阻断 PI3K/AKT 介导的氧化应激,从而减轻肾缺血和再灌注损伤诱导的纤维化
Authors Yang C, Chen Z, Yu H, Liu X
Received 26 July 2019
Accepted for publication 5 December 2019
Published 27 December 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 4375—4387
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S224909
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yan Zhu
Background: Ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury is a major cause of acute kidney injury, usually occurs during renal surgeries, and may eventually lead to chronic kidney diseases. However, effective therapeutic targets for renal I/R injury remain limited.
Purpose: In the present study, we investigated whether inhibition of disruptor of telomeric silencing 1-like (Dot1l) could alleviate renal I/R in vivo and in vitro, as well as the potential mechanisms involved in this process.
Methods: Sprague–Dawley rats were subjected to right renal ischemia for 45 mins and reperfusion for 0, 7, or 14 days with and without the Dot1l inhibitor EPZ004777. In addition, human renal proximal tubular epithelial cell line human kidney-2 cells were subjected to the hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R) process (ie, 3 hrs hypoxia, 12 hrs and 24 hrs reoxygenation), with or without Dot1l inhibitor or genetic knockdown.
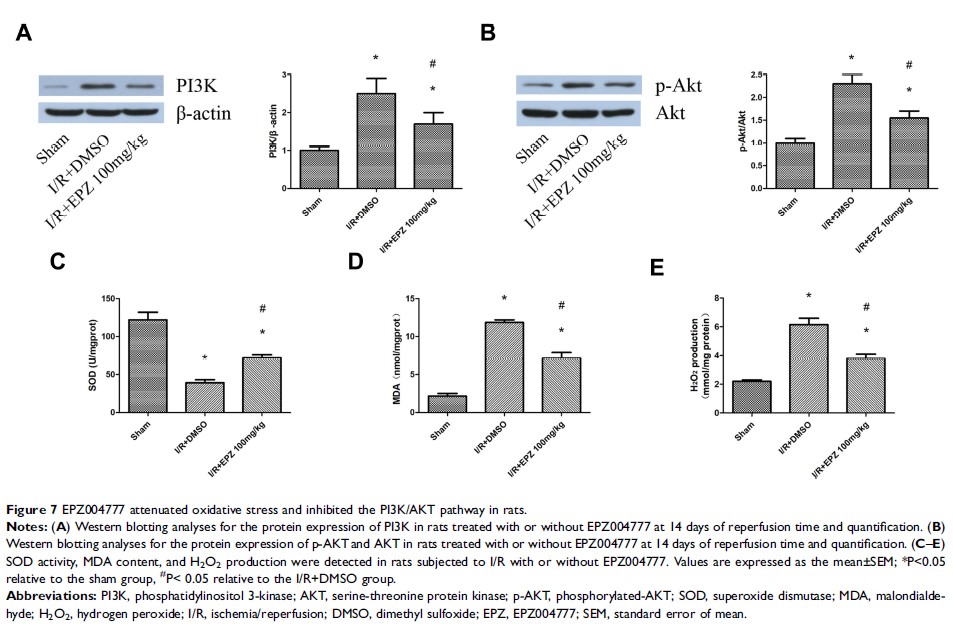
Results: Inhibition of Dot1l through EPZ004777 or genetic knockdown reduced the expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin, vimentin, and fibronectin in I/R- and H/R-induced injury. Moreover, H/R-induced fibrosis depended on oxidative stress in vitro. In addition, I/R- and H/R-induced generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) was attenuated by EPZ004777 or small interfering RNA for Dot1l. Furthermore, the elevation of ROS induced by Dot1l was regulated via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and serine-threonine protein kinase (AKT) phosphorylation in vivo and in vitro.
Conclusion: Inhibition of Dot1l alleviated renal fibrosis by preventing the generation of ROS via the PI3K/AKT pathway. These results indicate that inhibitor of Dot1l could be a potential therapeutic target for renal I/R injury.
Keywords: disruptor of telomeric silencing 1-like, ischemia and reperfusion, oxidative stress, fibrosis