110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

中期因子是膀胱镜微血尿无创检测中的潜在尿液生物标志物
Authors Lin H, Zhou Q, Wu W, Ma Y
Received 18 October 2019
Accepted for publication 12 December 2019
Published 3 January 2020 Volume 2019:12 Pages 11765—11775
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S235134
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Takuya Aoki
Background: To determine the role of Midkine (MDK) in non-invasive detection of bladder cancer (Bca) and the relationship with Ki67.
Methods: Sixty-five Bca patients and 55 non-Bca patients or healthy volunteers were enrolled and voided urine samples were prospectively obtained on the first day of enrollment. Tissue samples were collected by surgery. MDK and Ki67 expressions were analyzed by immunohistochemistry and Western Blot (WB). Specificity and sensitivity of MDK mRNA testing in the detection of Bca were determined by Receiver Operating Characteristic curve (ROC). The relationship between MDK and Ki67 was also assessed.
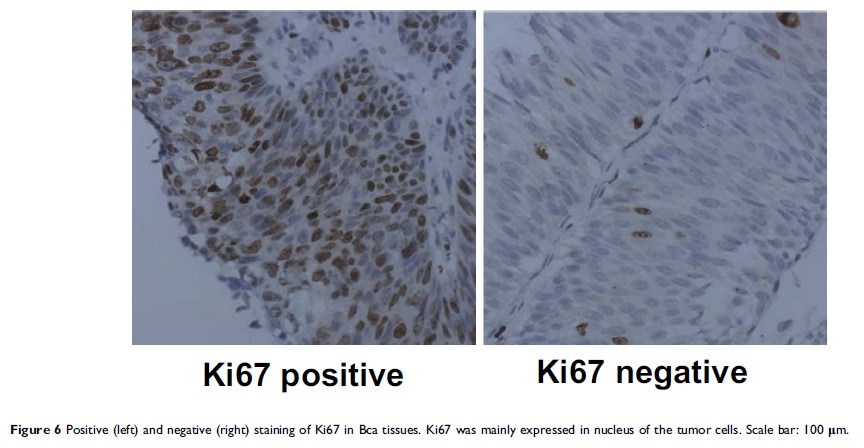
Results: MDK was overexpressed in Bca tissues than that in the non-cancer tissues. The specificity and sensitivity for MDK mRNA testing in urine in the identification of Bca was 80% and 72.3%. MDK detected 85.7% of high-grade tumors, 87.5% of muscle-invasive tumors and 79.4% of tumors larger than 3 cm in patients without gross hematuria. Microscopic hematuria may even increase the detection rate of Bca by MDK testing. Furthermore, the correlation of MDK and Ki67 was found positive.
Conclusion: MDK was overexpressed in Bca tissues and positively correlated with Ki67. MDK might be a potential biomarker for the detection of Bca, especially for those without gross hematuria but with microscopic hematuria.
Keywords: Midkine, non-invasive detection, bladder cancer, biomarker, Ki67