110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

黄芩苷对 6-OHDA 诱导的帕金森病模型的神经保护作用和机制
Authors Tu L, Wu ZY, Yang XL, Zhang Q, Gu R, Wang Q, Tian T, Yao H, Qu X, Tian JY
Received 20 February 2018
Accepted for publication 28 June 2018
Published 3 January 2020 Volume 2019:15 Pages 3615—3625
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S165931
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Wai Kwong Tang
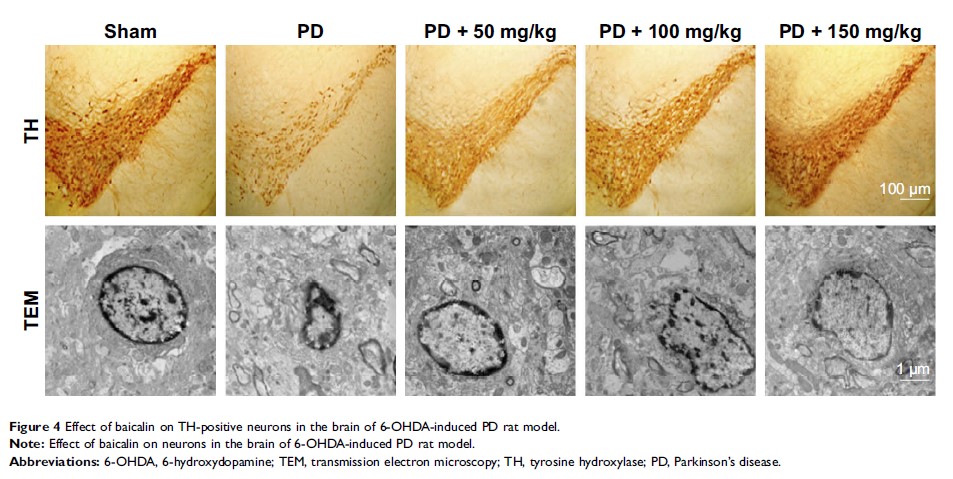
Objective: This research was aimed to investigate the effects of baicalin on 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)-induced rat model of Parkinson’s disease (PD) and the main mechanism of baicalin based on metabolomics.
Methods: The rat model of PD was induced by 6-OHDA. The protective effects of baicalin on rat model of PD were evaluated by open field test and rotarod test. The anti-PD efficacy of baicalin was evaluated by examining the morphologic changes of neurons and the level of monoamine neurotransmitters in the striatum, the number and morphology of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)-positive neurons, and oxidative stress. Combined with metabolomics methods, the pharmacodynamic mechanism of baicalin on PD pathogenesis was also explored.
Results: Baicalin treatment improved the rod time and voluntary movement in rat model of PD (P <0.05) by the open field test and rotarod test. In addition, baicalin also protected from oxidative stress injury (P <0.05), and regulated the content of monoamine neurotransmitters dopamine, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, 5-hydroxytryptamine, and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (P <0.05) and the number and morphology of TH-positive cells in 6-OHDA-induced PD model rats. By metabolomics, multivariate statistical analysis, and receiver operating characteristic curve analysis, we found that two metabolites N-acetyl aspartic acid and glutamic acid had a good diagnostic value. Quantitative analysis of metabolites showed a regulatory function of baicalin.
Conclusion: Baicalin has significant protective effect on 6-OHDA-induced PD rats, which may play a protective role through an antioxidant, promoting the release of neurotransmitters and regulating the metabolism of N-acetyl aspartate and glutamate.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease, neurotransmitter, baicalin, metabolomics