110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

薯蓣皂素(Dioscin)通过促进 c-myc 泛素化及随后的己糖激酶-2 遏制,来抑制结直肠癌的糖酵解并诱导细胞凋亡
Authors Wu Z, Han X, Tan G, Zhu Q, Chen H, Xia Y, Gong J, Wang Z, Wang Y, Yan J
Received 22 July 2019
Accepted for publication 6 December 2019
Published 6 January 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 31—44
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S224062
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Jianmin Xu
Purpose: Dioscin is a natural product isolated from traditional Chinese medicines and is reported to have antitumor activities against several cancers. In the present study, we aimed to investigate its potency against colorectal cancers, especially the effects on tumor glycolysis, and to elaborate related molecular mechanisms.
Methods: The antitumor activities of dioscin were evaluated by cell proliferation assays and colony formation assays in vitro and the mouse xenograft models in vivo. The effects of dioscin on tumor glycolysis were determined by measuring glucose absorption and lactate generation. Cell apoptosis was detected by cleaved PARP and the activity of caspase-3. Protein overexpression or gene knockdown was conducted to illustrate molecular mechanisms. Immunoprecipitation experiments were applied to identify the interaction between different proteins.
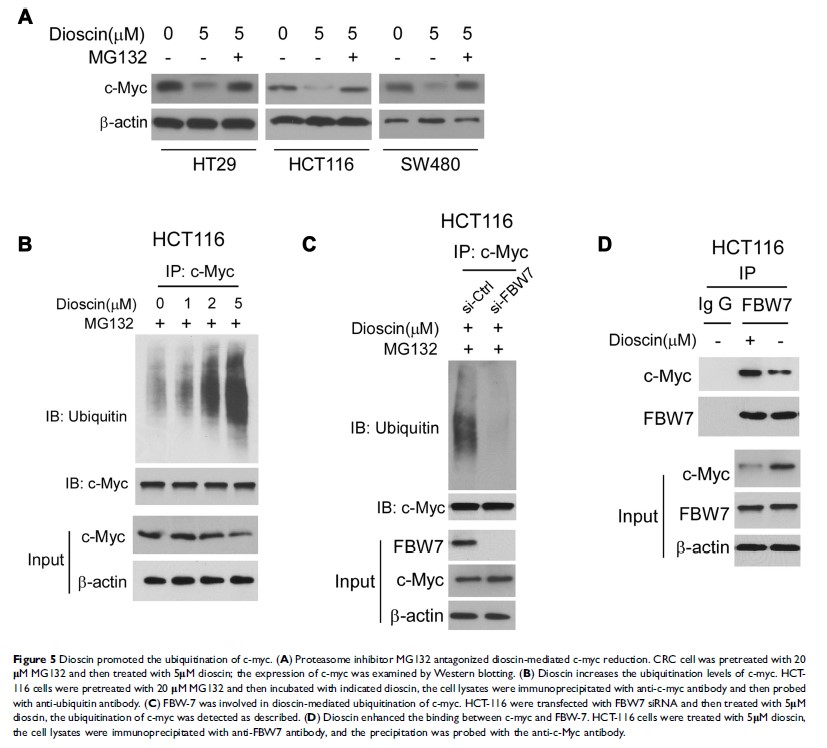
Results: Dioscin substantially inhibited colorectal cancer cell proliferation in vitro and suppressed the xenograft growth in nude mice. After dioscin treatment, with the suppression of hexokinase-2, the tumor glycolysis was significantly decreased. Dioscin substantially impaired the interaction between hexokinase-2 and VDAC-1, and induced cell apoptosis. Exogenous overexpression of hexokinase-2 significantly antagonized the glycolysis suppression and apoptosis induction by dioscin. Through enhancing the binding of E3 ligase FBW7 to c-myc, dioscin promoted the ubiquitination of c-myc and gave rise to c-myc degradation, which contributed to the inhibition of hexokinase-2.
Conclusion: Our studies revealed a novel mechanism by which dioscin exerted its antitumor activity in colorectal cancer, and verified that dioscin or its analog might have potentials for colorectal cancer therapy.
Keywords: colorectal cancer, tumor glycolysis, hexokinase-2, c-myc, ubiquitination