110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

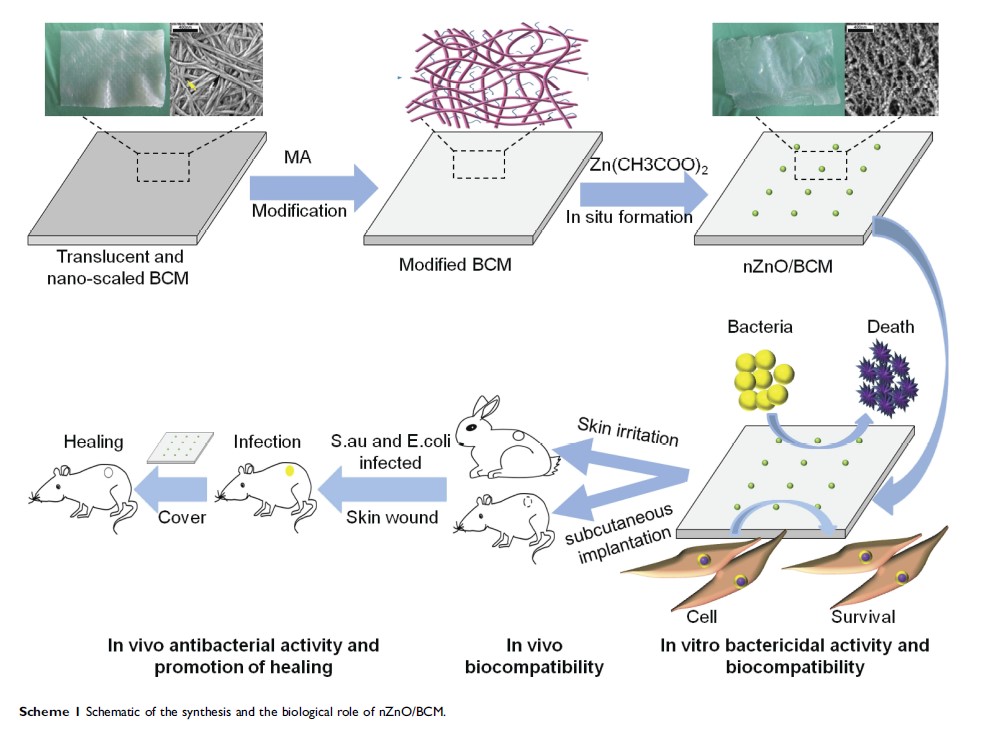
原位制备以 MA 修饰的细菌纤维素膜为基础的纳米 ZnO/BCM 生物复合材料,用于抗菌和伤口愈合
Authors Luo Z, Liu J, Lin H, Ren X, Tian H, Liang Y, Wang W, Wang Y, Yin M, Huang Y, Zhang J
Received 18 September 2019
Accepted for publication 16 December 2019
Published 6 January 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 1—15
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S231556
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: Developing an ideal wound dressing that meets the multiple demands of safe and practical, good biocompatibility, superior mechanical property and excellent antibacterial activity is highly desirable for wound healing. Bacterial cellulose (BC) is one of such promising class of biopolymers since it can control wound exudates and can provide moist environment to a wound resulting in better wound healing. However, the lack of antibacterial activity has limited its application.
Methods and Results: We prepared a flexible dressing based on a bacterial cellulose membrane and then modified it by chemical crosslinking to prepare in situ synthesis of nZnO/BCM via a facile and eco-friendly approach. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) results indicated that nZnO/BCM membranes were characterized by an ideal porous structure (pore size: 30∼ 90 μm), forming a unique string-beaded morphology. The average water vapor transmission of nZnO/BCM was 2856.60 g/m2/day, which improved the moist environment of nZnO/BCM. ATR-FITR further confirmed the stepwise deposition of nano-zinc oxide. Tensile testing indicated that our nanocomposites were flexible, comfortable and resilient. Bacterial suspension assay and plate counting methods demonstrated that 5wt. % nZnO/BCM possessed excellent antibacterial activity against S.aureus and E. coli , while MTT assay demonstrated that they had no measurable cytotoxicity toward mammalian cells. Moreover, skin irritation test and histocompatibility examination supported that 5wt. % nZnO/BCM had no stimulation to skin and had acceptable biocompatibility with little infiltration of the inflammatory cells. Finally, by using a bacteria-infected (S. aureus and E. coli ) murine wound model, we found that nZnO/BCM could prevent in vivo bacterial infections and promote wound healing via accelerating the re-epithelialization and wound contraction, and these membranes had no obvious toxicity toward normal tissues.
Conclusion: Therefore, the constructed nZnO/BCM has great potential for biomedical applications as an efficient antibacterial wound dressing.
Keywords: bacterial cellulose, nano-zinc oxide, in situ synthesis, antibacterial, non-toxicity, wound dressing