110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

PD-1/PD-L1 阻断剂在癌症免疫周期中的抵抗机制
Authors Zhuang Y, Liu C, Liu J, Li G
Received 20 November 2019
Accepted for publication 16 December 2019
Published 7 January 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 83—94
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S239398
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
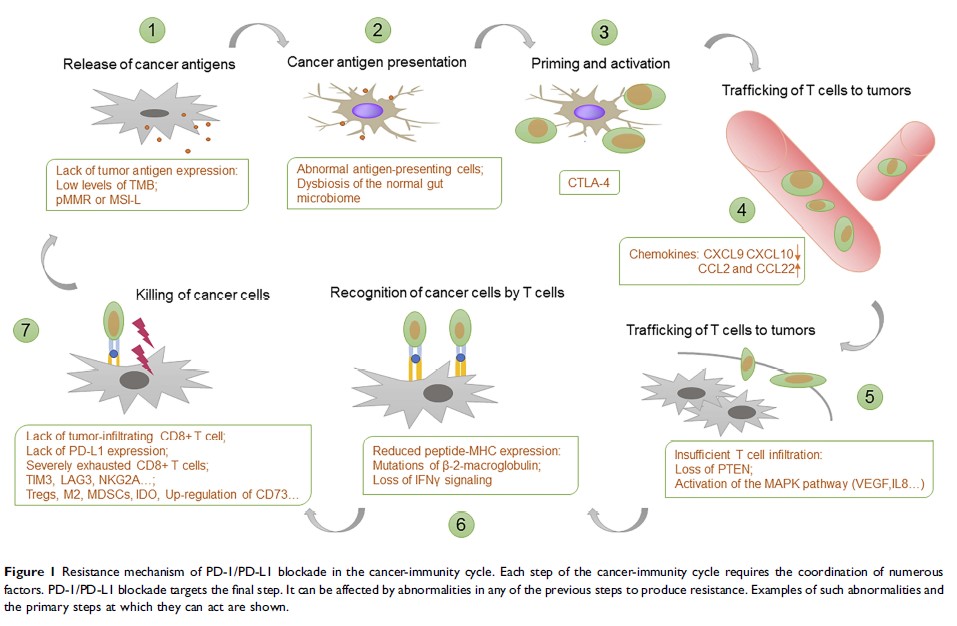
Abstract: In recent years, the PD-1/PD-L1 axis blockade has become a very promising therapy with significant clinical benefits for multiple tumor types. However, some patients still do not respond sufficiently to PD-1/PD-L1 targeted monotherapy. Therefore, investigating the mechanism of PD-1 blockade resistance will assist in exploring new immunotherapy strategies, controlling the progress of the disease, and thus bringing more sustainable survival benefits to patients. The tumor-immune cycle is divided into the following seven steps: the release of cancer antigens, cancer antigen presentation, priming and activation, trafficking of T cells to tumors, infiltration of T cells into tumors, recognition of cancer cells by T cells, and killing of cancer cells. Given that PD-1/PD-L1 blockade is primarily involved in step 7, any abnormalities in the previous steps may affect the efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors and lead to drug resistance. This review discussed the resistance mechanisms of PD-1/PD-L1 blockade in each cancer-immunity step to finding a more suitable treatment population and an optimized combination therapy to exert immunotherapy in tumor treatment to a greater extent.
Keywords: immunotherapy, PD-1, PD-L1, resistance