110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

葛根素抗癌活性的分子机制
Authors Ahmad B, Khan S, Liu Y, Xue M, Nabi G, Kumar S, Alshwmi M, Qarluq AW
Received 5 October 2019
Accepted for publication 16 December 2019
Published 8 January 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 79—90
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S233567
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eileen O'Reilly
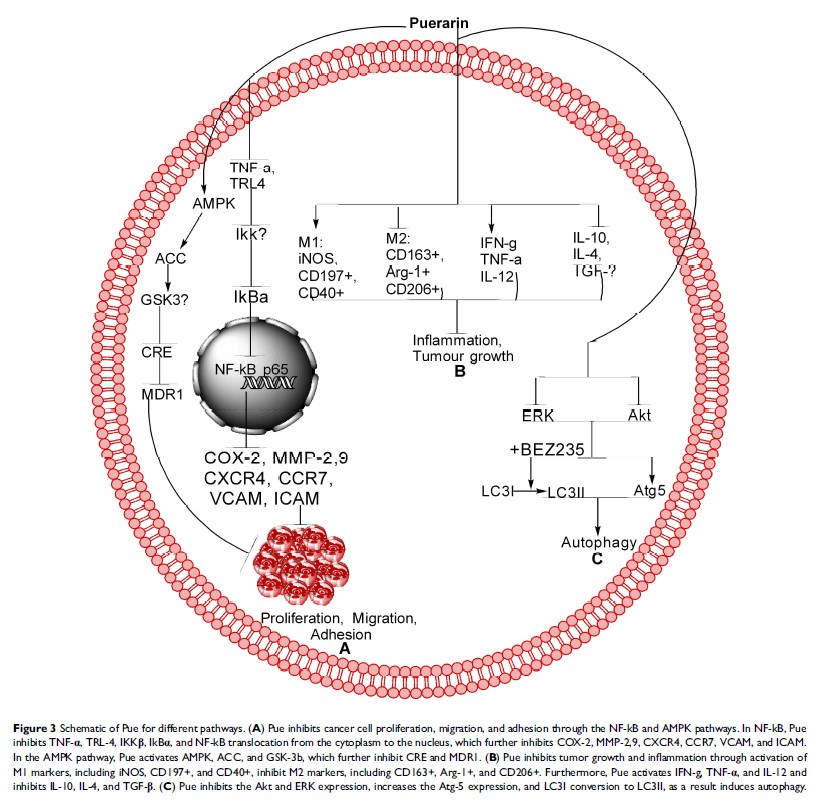
Abstract: Medicinal plants are a vital source of natural products (NPs) that can cure cancer through modulation of different pathways, including oxidative stress, extrinsic and intrinsic apoptosis, cell cycle, inflammation, NF-kB, PI3K/AKT/mTOR, AMPK (JNK), MEK/ERK (Raf)-MEK-ERK and autophagy. Puerarin (Pue), an important NP belonging to the isoflavone glycoside group, is derived from Pueraria lobata (Willd.) Ohwi, Pueraria thomsonii Benth, and Pueraria tuberosa (Willd.). This NP was approved by the Chinese Ministry of Health for the treatment of different diseases in 1993, but it was also later reported to exhibit anticancer activity. Pue causes cancer cells death through modulation of different mechanisms including oxidative stress, intrinsic and extrinsic, Survivin and XIAP, PI3K/AKT/mTOR, Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK, JNK, cell cycle, AMPK, NF-kB, inflammation and autophagy pathways. Therefore, this review compiles for the first time the studies about the anticancer mechanism of Pue and provides comprehensive information about the anticancer effects of Pue. This review may serve as a basis for future research and clinical treatment.
Keywords: medicinal plants, natural products, Puerarin, Pueraria lobata , Pueraria thomsonii , Pueraria tuberosa